Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Pharmacological Inhibition Decreases Alveolar Bone Loss by Modulating Host Inflammatory Response, RANK-Related Signaling, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Apoptosis
- PMID: 28356494
- PMCID: PMC5443319
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.116.238113
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Pharmacological Inhibition Decreases Alveolar Bone Loss by Modulating Host Inflammatory Response, RANK-Related Signaling, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Apoptosis
Abstract
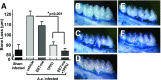
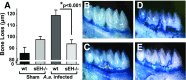
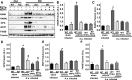
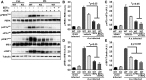
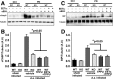
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), metabolites of arachidonic acid derived from the cytochrome P450 enzymes, are mainly metabolized by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) to their corresponding diols. EETs but not their diols, have anti-inflammatory properties, and inhibition of sEH might provide protective effects against inflammatory bone loss. Thus, in the present study, we tested the selective sEH inhibitor, 1-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-3-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl) urea (TPPU), in a mouse model of periodontitis induced by infection with Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Oral treatment of wild-type mice with TPPU and sEH knockout (KO) animals showed reduced bone loss induced by A. actinomycetemcomitans This was associated with decreased expression of key osteoclastogenic molecules, receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB/RANK ligand/osteoprotegerin, and the chemokine monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in the gingival tissue without affecting bacterial counts. In addition, downstream kinases p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase known to be activated in response to inflammatory signals were abrogated after TPPU treatment or in sEH KO mice. Moreover, endoplasmic reticulum stress was elevated in periodontal disease but was abrogated after TPPU treatment and in sEH knockout mice. Together, these results demonstrated that sEH pharmacological inhibition may be of therapeutic value in periodontitis.
Copyright © 2017 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

