Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic modelling of intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth and kill rates is predictive of clinical treatment duration
- PMID: 28356552
- PMCID: PMC5428680
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00529-6
Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic modelling of intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth and kill rates is predictive of clinical treatment duration
Abstract
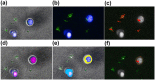
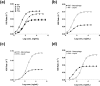
Tuberculosis (TB) treatment is long and complex, typically involving a combination of drugs taken for 6 months. Improved drug regimens to shorten and simplify treatment are urgently required, however a major challenge to TB drug development is the lack of predictive pre-clinical tools. To address this deficiency, we have adopted a new high-content imaging-based approach capable of defining the killing kinetics of first line anti-TB drugs against intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) residing inside macrophages. Through use of this pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) approach we demonstrate that the killing dynamics of the intracellular Mtb sub-population is critical to predicting clinical TB treatment duration. Integrated modelling of intracellular Mtb killing alongside conventional extracellular Mtb killing data, generates the biphasic responses typical of those described clinically. Our model supports the hypothesis that the use of higher doses of rifampicin (35 mg/kg) will significantly reduce treatment duration. Our described PK-PD approach offers a much needed decision making tool for the identification and prioritisation of new therapies which have the potential to reduce TB treatment duration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2015 (World Health Organisation, 2015).
-
- Gumbo, T., Lenaerts, A. J., Hanna, D., Romero, K. & Nuermberger, E. Nonclinical models for antituberculosis drug development: a landscape analysis. The Journal of infectious diseases211 Suppl 3, S83–S95, 10.1093/infdis/jiv183 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Muliaditan, M., Davies, G. R., Simonsson, U. S., Gillespie, S. H. & Della Pasqua, O. The implications of model-informed drug discovery and development for tuberculosis. Drug Discov Today, doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2016.09.004 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

