The role of metabolic reprogramming in T cell fate and function
- PMID: 28356677
- PMCID: PMC5367635
The role of metabolic reprogramming in T cell fate and function
Abstract
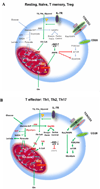
T lymphocytes undergo extensive changes in their metabolic properties during their transition through various differentiation states, from naïve to effector to memory or regulatory roles. The cause and effect relationship between metabolism and differentiation is a field of intense investigation. Many recent studies demonstrate the dependency of T cell functional outcomes on metabolic pathways and the possibility of metabolic intervention to modify these functions. In this review, we describe the basic metabolic features of T cells and new findings on how these correlate with various differentiation fates and functions. We also highlight the latest information regarding the main factors that affect T cell metabolic reprogramming.
Keywords: T lymphocytes; differentiation fate and function; metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT The authors have no competing conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
