Synergistic protective effect of N-acetylcysteine and taurine against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 28356716
- PMCID: PMC5367759
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S131316
Synergistic protective effect of N-acetylcysteine and taurine against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats
Abstract
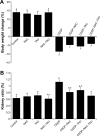
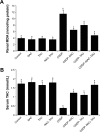
Cisplatin (cis-diaminedichloroplatinum II; CDDP) is an effective anticancer drug, but it has limitations because of its nephrotoxicity. This study investigates the protective effect of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and taurine (TAU), both individually and in combination, against CDDP nephrotoxicity in rats. For this purpose, 48 male rats were assigned into eight groups (n=6) as follows: 1) control group, 2) NAC group, 3) TAU group, 4) NAC-TAU group, 5) CDDP group, 6) CDDP-NAC group, 7) CDDP-TAU group, and 8) CDDP-NAC-TAU group. Cisplatin was administered as a single intraperitoneal injection at a concentration of 6 mg/kg. Three days after CDDP administration, NAC (50 mg/kg) and/or TAU (50 mg/kg) were administered three times weekly for four consecutive weeks. Kidney function markers in serum, urinary glucose and protein, as well as oxidant and antioxidant parameters in renal tissue were assessed. Administration of CDDP significantly elevated urinary glucose and protein, as well as serum creatinine, urea, and uric acid. Moreover, CDDP enhanced lipid peroxidation and suppressed the major enzymatic antioxidants in the kidney tissue. Treatment with NAC or TAU protected against the alterations in the serum, urine, and renal tissue when used individually along with CDDP. Furthermore, a combined therapy of both was more effective in ameliorating CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity, which points out to their synergistic effect.
Keywords: N-acetylcysteine; cisplatin; nephrotoxicity; oxidative stress; taurine.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang J, Wang L, Xing Z, et al. Status of bi- and multi-nuclear platinum anticancer drug development. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2010;10(4):272–282. - PubMed
-
- Ali BH, Al-Moundhri MS. Agents ameliorating or augmenting the nephrotoxicity of cisplatin and other platinum compounds. Food Chem Toxicol. 2006;44(8):1173–1183. - PubMed
-
- Humanes B, Lazaro A, Camano S, et al. Cilastatin protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity without compromising its anticancer efficiency in rats. Kidney Int. 2012;82(6):652–663. - PubMed
-
- Siddik ZH. Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene. 2003;22(47):7265–7279. - PubMed
-
- Hagar H, El-Medany A, Salam R, El-Medany G, Nayal O. Betaine supplementation mitigates cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity by abrogation of oxidative/nitrosative stress and suppression of inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2015;67(2):133–141. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

