Laser thermal ablation of multidrug-resistant bacteria using functionalized gold nanoparticles
- PMID: 28356741
- PMCID: PMC5367598
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S124778
Laser thermal ablation of multidrug-resistant bacteria using functionalized gold nanoparticles
Abstract
The issue of multidrug resistance (MDR) has become an increasing threat to public health. One alternative strategy against MDR bacteria would be to construct therapeutic vectors capable of physically damaging these microorganisms. Gold nanoparticles hold great promise for the development of such therapeutic agents, since the nanoparticles exhibit impressive properties, of which the most important is the ability to convert light into heat. This property has scientific significance since is exploited to develop nano-photothermal vectors to destroy bacteria at a molecular level. The present paper summarizes the latest advancements in the field of nanotargeted laser hyperthermia of MDR bacteria mediated by gold nanoparticles.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; bacteria; gold nanoparticles; photo-thermal ablation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
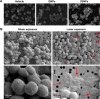

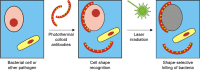
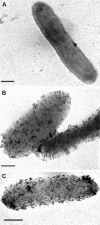
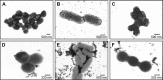
References
-
- Giedraitienė A, Vitkauskienė A, Naginienė R, Pavilonis A. Antibiotic resistance mechanisms of clinically important bacteria. Medicina (kaunas) 2011;47(13):137–146. - PubMed
-
- Smith R, Coast J. The true cost of antimicrobial resistance. BMJ. 2013;346:f1493. - PubMed
-
- Veerapandian M, Yun K. Functionalization of biomolecules on nanoparticles: specialized for antibacterial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;90(5):1655–1667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

