Significance of KRAS, NRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA mutations in metastatic colorectal cancer patients receiving Bevacizumab: a single institution experience
- PMID: 28356789
- PMCID: PMC4924637
- DOI: 10.6001/actamedica.v23i1.3267
Significance of KRAS, NRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA mutations in metastatic colorectal cancer patients receiving Bevacizumab: a single institution experience
Abstract
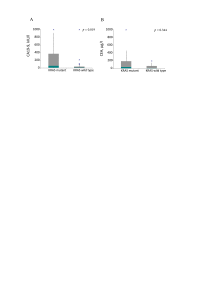
Background. KRAS mutation is an important predictive and prognostic factor for patients receiving anti-EGFR therapy. An expanded KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA mutation analysis provides additional prognostic information, but its role in predicting bevacizumab efficacy is unclear. The aim of our study was to evaluate the incidence of KRAS, NRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA mutations in metastatic colorectal cancer patients receiving first line oxaliplatin based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab and to evaluate their prognostic and predictive significance. Methods. 55 patients with the first-time diagnosed CRC receiving FOLFOX ± bevacizumab were involved in the study. Tumour blocks were tested for KRAS mutations in exons 2, 3 and 4, NRAS mutations in exons 2, 3 and 4, BRAF mutation in exon 15 and PIK3CA mutations in exons 9 and 20. The association between mutations and clinico-pathological factors, treatment outcomes and survival was analyzed. Results. KRAS mutations were detected in 67.3% of the patients, BRAF in 1.8%, PIK3CA in 5.5% and there were no NRAS mutations. A significant association between the high CA 19-9 level and KRAS mutation was detected (mean CA 19-9 levels were 276 and 87 kIU/l, respectively, p = 0.019). There was a significantly higher response rate in the KRAS, NRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA wild type cohort receiving bevacizumab compared to any gene mutant type (100 and 60%, respectively, p = 0.030). The univariate Cox regression analysis did not confirm KRAS and other tested mutations as prognostic factors for PFS or OS. Conclusions. Our study revealed higher KRAS and lower NRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA mutation rates in the Lithuanian population than those reported in the literature. KRAS mutation was associated with the high CA 19-9 level and mucinous histology type, but did not show any predictive or prognostic significance. The expanded KRAS, NRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA mutation analysis provided additional significant predictive information.
Santrauka Įvadas. Pacientams, kuriems taikomas gydymas anti- EGFR terapija, KRAS mutacijos – svarbus predikcinis ir prognozinis veiksnys. Išplėstinė KRAS, NRAS, BRAF ir PIK3CA analizė suteikia papildomos prognozinės informacijos, tačiau jos reikšmė nuspėjant gydymo bevacizumabu efektyvumą neaiški. Tyrimo tikslas – ištirti ir įvertinti KRAS, NRAS, BRAF ir PIK3CA mutacijų prognozinę bei predikcinę reikšmę pacientams, kuriems taikoma pirmos eilės chemoterapija oksaliplatinos pagrindu su bevacizumabu. Metodai. Tyrime dalyvavo 55 pacientai, jiems dėl metastazavusios ligos skirtas pirmos eilės gydymas FOLFOX4 schema su arba be bevacizumabo. Naviko medžiagoje, gautoje iš parafininių blokų, tirtos KRAS 2, 3 ir 4 egzono, NRAS 2, 3 ir 4 egzono, BRAF 15 egzono ir PIK3CA 9 ir 20 egzono mutacijos. Vertintas šių mutacijų ryšys su klinikinėmis ir patologinėmis charakteristikomis, atsaku į gydymą bei išgyvenamumu. Rezultatai. KRAS mutacijų nustatyta 67,3 %, BRAF – 1,8 %, PIK3CA – 5,5 % pacientų ir nė vienam neaptikta NRAS mutacijų. Pastebėtas reikšmingas ryšys tarp KRAS mutacijos ir CA 19–9 lygio (vidutinė CA 19–9 reikšmė buvo 276 kIU/l KRAS mutuotų pacientų grupėje, palyginti su 87 kIU/l laukinio tipo grupėje, p = 0,019). Nustatytas statistiškai geresnis atsakas pacientams, gydytiems chemoterapija su bevacizumabu, jiems nenustatyta jokių tirtųjų mutacijų, palyginti su tais, kuriems aptikta bent vieno tirtojo geno mutacija (atsako dažnis atitinkamai buvo 100 ir 60 %, p = 0,030). KRAS ar kitų mutacijų prognozinė reikšmė išgyvenamumui be ligos progresijos bei bendrajam išgyvenamumui atlikus vienamatę Cox regresijos analizę nebuvo patvirtinta. Išvados. Tyrimo metu nustatytas KRAS mutacijos dažnis yra didesnis, o NRAS, BRAF ir PIK3CA – mažesnis nei skelbiama literatūroje. KRAS mutacija buvo susijusi su didesniu CA 19–9 lygiu bei mucininio tipo navikais, tačiau neturėjo predikcinės ar prognozinės reikšmės. Išplėstinė KRAS, NRAS, BRAF ir PIK3CA mutacijų analizė suteikė reikšmingos papildomos predikcinės informacijos gydant FOLFOX4 ir bevacizumabo deriniu. Raktažodžiai: KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, storosios žarnos vėžys, bevacizumabas.
Santrauka Įvadas. Pacientams, kuriems taikomas gydymas anti- EGFR terapija, KRAS mutacijos – svarbus predikcinis ir prognozinis veiksnys. Išplėstinė KRAS, NRAS, BRAF ir PIK3CA analizė suteikia papildomos prognozinės informacijos, tačiau jos reikšmė nuspėjant gydymo bevacizumabu efektyvumą neaiški. Tyrimo tikslas – ištirti ir įvertinti KRAS, NRAS, BRAF ir PIK3CA mutacijų prognozinę bei predikcinę reikšmę pacientams, kuriems taikoma pirmos eilės chemoterapija oksaliplatinos pagrindu su bevacizumabu. Metodai. Tyrime dalyvavo 55 pacientai, jiems dėl metastazavusios ligos skirtas pirmos eilės gydymas FOLFOX4 schema su arba be bevacizumabo. Naviko medžiagoje, gautoje iš parafininių blokų, tirtos KRAS 2, 3 ir 4 egzono, NRAS 2, 3 ir 4 egzono, BRAF 15 egzono ir PIK3CA 9 ir 20 egzono mutacijos. Vertintas šių mutacijų ryšys su klinikinėmis ir patologinėmis charakteristikomis, atsaku į gydymą bei išgyvenamumu. Rezultatai. KRAS mutacijų nustatyta 67,3 %, BRAF – 1,8 %, PIK3CA – 5,5 % pacientų ir nė vienam neaptikta NRAS mutacijų. Pastebėtas reikšmingas ryšys tarp KRAS mutacijos ir CA 19–9 lygio (vidutinė CA 19–9 reikšmė buvo 276 kIU/l KRAS mutuotų pacientų grupėje, palyginti su 87 kIU/l laukinio tipo grupėje, p = 0,019). Nustatytas statistiškai geresnis atsakas pacientams, gydytiems chemoterapija su bevacizumabu, jiems nenustatyta jokių tirtųjų mutacijų, palyginti su tais, kuriems aptikta bent vieno tirtojo geno mutacija (atsako dažnis atitinkamai buvo 100 ir 60 %, p = 0,030). KRAS ar kitų mutacijų prognozinė reikšmė išgyvenamumui be ligos progresijos bei bendrajam išgyvenamumui atlikus vienamatę Cox regresijos analizę nebuvo patvirtinta. Išvados. Tyrimo metu nustatytas KRAS mutacijos dažnis yra didesnis, o NRAS, BRAF ir PIK3CA – mažesnis nei skelbiama literatūroje. KRAS mutacija buvo susijusi su didesniu CA 19–9 lygiu bei mucininio tipo navikais, tačiau neturėjo predikcinės ar prognozinės reikšmės. Išplėstinė KRAS, NRAS, BRAF ir PIK3CA mutacijų analizė suteikė reikšmingos papildomos predikcinės informacijos gydant FOLFOX4 ir bevacizumabo deriniu. Raktažodžiai: KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, storosios žarnos vėžys, bevacizumabas.
Keywords: BRAF; KRAS; NRAS; PIK3CA; bevacizumab; colorectal cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61: 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Smailytė G, Aleknavičienė B.. Vėžys Lietuvoje 2012 metais. Nacionalinis vėžio institutas, Vėžio registras; 2015.
-
- De Angelis R, Sant M, Coleman MP, Francisci S, Baili P, Pierannunzio D, et al.. Cancer survival in Europe 1999–2007 by country and age: results of EUROCARE-5 – a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15: 23–34. - PubMed
-
- Fodde R, Smits R, Clevers H.. APC, signal transduction and genetic instability in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001; 1: 55–67. - PubMed
-
- Danielsen SA, Eide PW, Nesbakken A. Portrait of the PI3K/AKT pathway in colorectal cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015; 1855: 104–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
