Prognostic Value and Daily Trend of Interleukin-6, Neutrophil CD64 Expression, C-Reactive Protein and Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein in Critically Ill Patients: Reliable Predictors of Outcome or Not?
- PMID: 28356852
- PMCID: PMC4922357
- DOI: 10.1515/jomb-2015-0002
Prognostic Value and Daily Trend of Interleukin-6, Neutrophil CD64 Expression, C-Reactive Protein and Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein in Critically Ill Patients: Reliable Predictors of Outcome or Not?
Abstract
Background: Severe sepsis and/or trauma complicated by multiple organ dysfunction syndrome are the leading causes of death in critically ill patients. The aim of this prospective single-centre study was to assess the prognostic value and daily trend of interleukin-6 (IL-6), neutrophil CD64 expression, C-reactive protein (CRP) and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) regarding outcome in critically ill patients with severe trauma and/or severe sepsis. Outcome measure was hospital mortality.
Methods: One hundred and two critically ill patients admitted to the intensive care unit of a tertiary university hospital were enrolled in this prospective study. Blood samples were collected on admission (day 1), days 2 and 3.
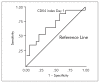
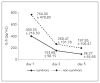
Results: CD64 index was 1.6-fold higher on day 1 and 1.78-fold higher on day 2 in non-survivors (p<0.05). The area under the curve (AUC) for the CD64 index on day 1 for outcome was 0.727. At a cut-off level of 2.80 sensitivity was 75% and specificity was 65%. Patients with CD64 index level on day 1 higher than 2.80 had 2.4-fold higher probability of dying. Odds ratio is 2.40; 95% CI 0.60-9.67.
Conclusions: CD64 index on day 1 is a fairly good predictor of outcome. AUCs for IL-6, CRP and LBP were < 0.55, suggesting these biomarkers failed to predict outcome.
Uvod: Teška sepsa i/ili trauma kod koje se kao komplikacija javlja sindrom multiple organske disfunkcije je vodeći uzrok smrti kod kritično obolelih. Cilj ove prospektivne studije je bio da se proceni prognostička vrednost i utvrdi kinetika inter-leukina-6 (IL-6), ekspresije CD64 na neutrofilima, C-reaktivnog proteina (CRP) i proteina koji vezuje lipopolisaharid (lipopolysaccharide-binding protein – LBP) u smislu ishoda kod kritično obolelih sa teškom traumom i/ili teškom sepsom. Mera ishoda je bio hospitalni mortalitet.
Metode: Sto dva kritično obolela pacijenta primljena u jedini-cu intenzivne terapije tercijarne univerzitetske bolnice su obu-hvaćena prospektivnom studijom. Uzorci krvi su sakupljani na dan prijema (dan 1), a zatim drugog i trećeg dana.
Rezultati: CD64 indeks je bio 1,6 puta viši prvog dana i 1,78 puta viši drugog dana kod umrlih (p<0,05). Vrednost AUC/ROC za CD64 indeks prvog dana u smislu predikcije ishoda je bila 0,727. Pri cut-off vrednosti od 2,80 senzitivnost je bila 75%, specifičnost 65% a OR 2,40 (95% CI 0,60–9,67). Pacijenti sa nivoom CD64 indeksa prvog dana višim od 2,80 imali su 2,4 puta veću verovatnoću smrtnog ishoda.
Zaključak: Vrednost CD64 indeksa prvog dana je dobar prediktor ishoda. AUC/ROC vrednosti za IL-6, CRP i LBP su bile < 0,55, pa se ovi biomarkeri nisu pokazali dobrim pre-diktorima ishoda.
Keywords: biomarkers; critical care; leukocytes; outcome; prognosis.
Figures



References
-
- Surbatovic M, Radakovic S, Jovanovic K, Romic P. New strategies in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome therapy for sepsis. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2005;133(7–8):3791.83. - PubMed
-
- Surbatovic M, Grujic K, Cikota B, Jevtic M, Filipovic N, Romic P, et al. Polymorphisms of genes encoding tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-10, cluster of differentiation-14 and interleukin-1ra in critically ill patients. J Crit Care. 2010;25(3):542.e1–8. - PubMed
-
- Morris AC, Simpson AJ, Walsh TS. Hyperinflammation and mediators of immune suppression in critical illness. In: Vincent JL, editor. Annual update in intensive care and emergency medicine. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 2013. pp. 135–44.
-
- Surbatovic M, Radakovic S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels early in severe acute pancreatitis: is there predictive value regarding severity and outcome? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;47(7):637–43. - PubMed
-
- Surbatovic M, Filipovic N, Radakovic S, Stankovic N, Slavkovic Z. Immune cytokine response in combat casualties: blast or explosive trauma with or without secondary sepsis. Mil Med. 2007;172(2):190–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
