Analysis of the Variability of Epstein-Barr Virus Genes in Infectious Mononucleosis: Investigation of the Potential Correlation with Biochemical Parameters of Hepatic Involvement
- PMID: 28356886
- PMCID: PMC5346813
- DOI: 10.1515/jomb-2015-0021
Analysis of the Variability of Epstein-Barr Virus Genes in Infectious Mononucleosis: Investigation of the Potential Correlation with Biochemical Parameters of Hepatic Involvement
Abstract
Background: Primary Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection is usually asymptomatic, although at times it results in the benign lymphoproliferative disease, infectious mononucleosis (IM), during which almost half of patients develop hepatitis. The aims of the present study are to evaluate polymorphisms of EBV genes circulating in IM isolates from this geographic region and to investigate the correlation of viral sequence patterns with the available IM biochemical parameters.
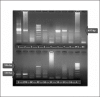
Methods: The study included plasma samples from 128 IM patients. The genes EBNA2, LMP1, and EBNA1 were amplified using nested-PCR. EBNA2 genotyping was performed by visualization of PCR products using gel electrophoresis. Investigation of LMP1 and EBNA1 included sequence, phylogenetic, and statistical analyses.
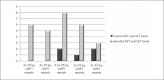
Results: The presence of EBV DNA in plasma samples showed correlation with patients' necessity for hospitalization (p=0.034). The majority of EBV isolates was genotype 1. LMP1 variability showed 4 known variants, and two new deletions (27-bp and 147-bp). Of the 3 analyzed attributes of LMP1 isolates, the number of 33-bp repeats less than the reference 4.5 was the only one that absolutely correlated with the elevated levels of transaminases. EBNA1 variability was presented by prototype subtypes. A particular combination of EBNA2, LMP1, and EBNA1 polymorphisms, deleted LMP1/P-thr and non-deleted LMP1/P-ala, as well as genotype 1/ 4.5 33-bp LMP1 repeats or genotype 2/ 4.5 33-bp LMP1 repeats showed correlation with elevated AST (aspartate aminotransferase) and ALT (alanine transaminase).
Conclusions: This is the first study which identified the association between EBV variability and biochemical parameters in IM patients. These results showed a possibility for the identification of hepatic related diagnostic EBV markers.
Uvod: Primarna infekcija koju izaziva Epštajn-Bar virus obično je asimptomatska. Povremeno, ova infekcija može se manifestovati benignim limfoproliferativnim oboljenjem, infektivnom mononukleozom (IM), za čije vreme polovina pacijenata dobije hepatitis. Ciljevi ove studije bili su evaluacija EBV genskih polimorfizama koji su zastupljeni u IM izolatima ovog geografskog područja, kao i ispitivanje korelacije specifične virusne varijabilnosti sa dostupnim jetrinim biohemijskim parametrima IM pacijenata.
Metode: Studija je uključila uzorke plazme od 128 IM pacijenata. Za umnožavanje EBNA2, LMP1 i EBNA1 gena korišćen je nested-PCR metod. EBNA2 genotipizacija izvršena je vizuelizacijom PCR produkata korišćenjem gel elektroforeze. LMP1 i EBNA1 ispitivanje obuhvatilo je analizu njihovih genskih sekvenci, a zatim i filogenetsku i statističku obradu.
Rezultati: Prisustvo EBV DNK u uzorcima plazme korelisalo je sa neophodnošću bolničkog lečenja pacijenata (p=0,034). Većina izolata pripadala je genotipu 1. Analizom LMP1 varijabilnosti dobijene su 4 poznate varijante i 2 nove delecije (27-bp i 147-bp). Među 3 ispitivane karakteristike LMP1 izolata, broj 33-bp ponovaka manji od referenta 4,5 jedini je bio apsolutno povezan sa povišenim nivoom aspartat aminotransferaze (AST) i alanin transaminaze (ALT). EBNA1 varijabilnost dala je samo prototipne subtipove. Specifične kombinacije EBNA2, LMP1 i EBNA1 polimorfizama, LMP1 sa delecijom/P-thr i LMP1 bez delecije/P-ala, kao i genotip1/≤4.5 33-bp LMP1 ponovka ili genotip 2/≤4.5 33-bp LMP1 ponovka, pokazale su korelaciju sa povišenim vrednostima transaminaza.
Zaključak: Ovo je prva studija u kojoj je identifikovana povezanost između EBV genetičke varijabilnosti i biohemijskih parametara IM pacijenata. Prikazani rezultati pokazuju mogućnost identifikovanja dijagnostičkih EBV markera povezanih sa statusom oštećenja jetre.
Keywords: EBV; LMP1; gene polymorphism; infectious mononucleosis; transaminase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors stated that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the Variability of Epstein-Barr Virus Genes in Nasopharyngeal Biopsies: Potential Predictors for Carcinoma Progression.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 12;11(4):e0153498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153498. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27071030 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxy-terminal sequence variation of LMP1 gene in Epstein-Barr-virus-associated mononucleosis and tumors from Serbian patients.J Med Virol. 2012 Apr;84(4):632-42. doi: 10.1002/jmv.23217. J Med Virol. 2012. PMID: 22337303
-
The sequence analysis of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA1 gene: could viral screening markers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma be identified?Med Microbiol Immunol. 2019 Feb;208(1):81-88. doi: 10.1007/s00430-018-0561-2. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30203133
-
Distribution, persistence and interchange of Epstein-Barr virus strains among PBMC, plasma and saliva of primary infection subjects.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 25;10(3):e0120710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120710. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25807555 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive Epstein-Barr virus variants associated with benign and malignant pediatric pathologies: LMP1 sequence characterization and linkage with other viral gene polymorphisms.J Clin Microbiol. 2012 Mar;50(3):609-18. doi: 10.1128/JCM.05778-11. Epub 2012 Jan 11. J Clin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22205789 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Are Selected Cytokines and Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Load Predictors of Hepatological Complications of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Children?J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 24;12(19):6158. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196158. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37834802 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1 Variants in Patients with Infectious Mononucleosis and Association with Selected Biochemical and Hematological Parameters.Pathogens. 2023 Jul 6;12(7):915. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12070915. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37513762 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation as a New Predictor of Achieving Remission or Lupus Low Disease Activity State in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Cutaneous Involvement.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 24;24(7):6156. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076156. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047126 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterisation of Epstein-Barr Virus in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 9;23(24):15635. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415635. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555277 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence variations of Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene in gastric cancer and chronic gastritis isolates from Iranian patients.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2022 Summer;15(3):225-231. doi: 10.22037/ghfbb.v15i3.2578. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2022. PMID: 36311962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rickinson AB, Kieff E. Knipe D, Howlry P. Fields Virology. 5th edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. Epstein-Barr Virus and Its Replication; pp. 2603–54.
-
- Young LS, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:757–68. - PubMed
-
- Markin RS. Manifestations of Epstein-Barr virus-associated disorders in liver. Liver. 1994;14:1–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
