Random Deep Belief Networks for Recognizing Emotions from Speech Signals
- PMID: 28356908
- PMCID: PMC5357547
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/1945630
Random Deep Belief Networks for Recognizing Emotions from Speech Signals
Abstract
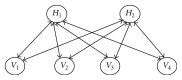
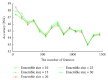
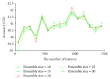
Now the human emotions can be recognized from speech signals using machine learning methods; however, they are challenged by the lower recognition accuracies in real applications due to lack of the rich representation ability. Deep belief networks (DBN) can automatically discover the multiple levels of representations in speech signals. To make full of its advantages, this paper presents an ensemble of random deep belief networks (RDBN) method for speech emotion recognition. It firstly extracts the low level features of the input speech signal and then applies them to construct lots of random subspaces. Each random subspace is then provided for DBN to yield the higher level features as the input of the classifier to output an emotion label. All outputted emotion labels are then fused through the majority voting to decide the final emotion label for the input speech signal. The conducted experimental results on benchmark speech emotion databases show that RDBN has better accuracy than the compared methods for speech emotion recognition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Emotion Recognition from Chinese Speech for Smart Affective Services Using a Combination of SVM and DBN.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Jul 24;17(7):1694. doi: 10.3390/s17071694. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28737705 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern Recognition Methods and Features Selection for Speech Emotion Recognition System.ScientificWorldJournal. 2015;2015:573068. doi: 10.1155/2015/573068. Epub 2015 Aug 4. ScientificWorldJournal. 2015. PMID: 26346654 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of Emotions Using Multichannel EEG Data and DBN-GC-Based Ensemble Deep Learning Framework.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2018 Dec 13;2018:9750904. doi: 10.1155/2018/9750904. eCollection 2018. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30647727 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in real-life emotion annotation and machine learning based detection.Neural Netw. 2005 May;18(4):407-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2005.03.007. Neural Netw. 2005. PMID: 15993746 Review.
-
Automated emotion recognition: Current trends and future perspectives.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022 Mar;215:106646. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106646. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022. PMID: 35093645 Review.
Cited by
-
An enhanced speech emotion recognition using vision transformer.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 7;14(1):13126. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63776-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38849422 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning-based EEG emotion recognition: Current trends and future perspectives.Front Psychol. 2023 Feb 27;14:1126994. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1126994. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36923142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emotion Probe: On the Universality of Cross-Linguistic and Cross-Gender Speech Emotion Recognition via Machine Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Mar 23;22(7):2461. doi: 10.3390/s22072461. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35408076 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional parallel echo state network for speech emotion recognition.Neural Comput Appl. 2022;34(20):17581-17599. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07410-2. Epub 2022 May 31. Neural Comput Appl. 2022. PMID: 35669535 Free PMC article.
-
Survey on Deep Neural Networks in Speech and Vision Systems.Neurocomputing (Amst). 2020 Dec 5;417:302-321. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.07.053. Epub 2020 Jul 26. Neurocomputing (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33100581 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fong B., Westerink J. Affective computing in consumer electronics. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing. 2012;3(2):129–131. doi: 10.1109/T-AFFC.2012.20. - DOI
-
- El Ayadi M., Kamel M. S., Karray F. Survey on speech emotion recognition: features, classification schemes, and databases. Pattern Recognition. 2011;44(3):572–587. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2010.09.020. - DOI
-
- Harimi A., AhmadyFard A., Shahzadi A., Yaghmaie K. Anger or joy? Emotion recognition using nonlinear dynamics of speech. Applied Artificial Intelligence. 2015;29(7):675–696. doi: 10.1080/08839514.2015.1051891. - DOI
-
- Sun Y., Wen G. Ensemble softmax regression model for speech emotion recognition. Multimedia Tools and Applications. 2016:1–24. doi: 10.1007/s11042-016-3487-y. - DOI
-
- Park J.-S., Kim J.-H., Oh Y.-H. Feature vector classification based speech emotion recognition for service robots. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics. 2009;55(3):1590–1596. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2009.5278031. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

