Wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 is a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in bladder transitional cell carcinoma
- PMID: 28356972
- PMCID: PMC5351345
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.5475
Wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 is a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in bladder transitional cell carcinoma
Abstract
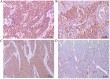
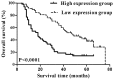
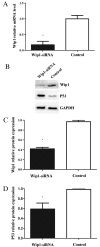
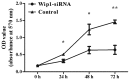
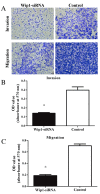
Wild-type p53-induced phosphatase (Wip1) is an established oncogene and is associated with development of multiple forms of human cancer. However, the expression and role of Wip1 in human bladder transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) remains to be elucidated. In the present study, immunohistochemistry demonstrated that Wip1 was overexpressed in bladder TCC tissues compared with corresponding normal bladder tissues in 106 bladder TCC cases (P<0.0001). Furthermore, high expression levels of Wip1 were significantly associated with increasing tumor size (P=0.002), pathological grade (P=0.025), clinical T stage (P=0.001) and lymph nodal metastasis (P=0.003). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis identified that patients with high Wip1 expression levels exhibited a lower overall survival time (P<0.0001), and Cox proportional hazards regression model analysis demonstrated that Wip1 expression was an independent prognostic factor in patients with bladder TCC (P=0.025). In addition, downregulation of Wip1 expression by transfection with small interfering RNA in bladder cancer cells inhibited cell proliferation, invasion and migration (P<0.05), along with the upregulation of p53 protein levels (P<0.05). These findings suggest that Wip1 may function as a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target in bladder cancer.
Keywords: Wip1; bladder transitional cell carcinoma; invasion; migration; prognosis; proliferation.
Figures
References
-
- Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R, Groshen S, Feng AC, Boyd S, Skinner E, Bochner B, Thangathurai D, Mikhail M, et al. Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: Long-term results in 1054 patients. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:666–675. - PubMed
-
- Fiscella M, Zhang H, Fan S, Sakaguchi K, Shen S, Mercer WE, Woude GF Vande, O'Connor PM, Appella E. Wip1, a novel human protein phosphatase that is induced in response to ionizing radiation in a p53-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:6048–6053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
