Molecular mechanisms of cholangiocarcinoma cell inhibition by medicinal plants
- PMID: 28356985
- PMCID: PMC5351256
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.5488
Molecular mechanisms of cholangiocarcinoma cell inhibition by medicinal plants
Abstract
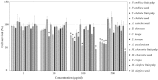
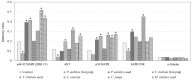
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is one of the most common causes of cancer-associated mortality in Thailand. Certain phytochemicals have been demonstrated to modulate apoptotic signaling pathways, which may be targeted for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of specific medicinal plants on the inhibition of CCA cell proliferation, and to identify the molecular mechanisms underlying this. A WST-1 cell proliferation assay was performed using an RMCCA1 cell line, and apoptotic signaling pathways were also investigated using a PathScan Stress and Apoptosis Signaling Antibody Array Kit. The cell proliferation assay indicated that extracts from the Phyllanthus emblica fruit pulp (PEf), Phyllanthus emblica seed (PEs), Terminalia chebula fruit pulp (TCf), Terminalia chebula seed (TCs), Areca catechu seed (ACs), Curcuma longa (CL) and Moringa oleifera seed (MOs) exerted anti-proliferative activity in RMCCA1 cells. In addition, the PathScan assay revealed that certain pro-apoptotic molecules, including caspase-3, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, checkpoint kinase 2 and tumor protein 53, exhibited increased activity in RMCCA1 cells treated with the aforementioned selected plant extracts, with the exception of PEf. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways (including ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK) expression level was significantly increased in RMCCA1 cells pre-treated with extracts of PEs, TCf, CL and MOs. The activation of protein kinase B (Akt) was significantly demonstrated in RMCCA1 cells pre-treated with extracts of TCf, ACs and MOs. In summary, the present study demonstrated that extracts of PEs, TCf, TCs, ACs, CL and MOs exhibited anti-proliferative effects in CCA cells by inducing pro-apoptotic signals and modulating signal transduction molecules. Further studies in vivo are required to demonstrate the potential applications of specific plant extracts for the treatment of human cancer.
Keywords: anticancer; apoptosis; cholangiocarcinoma; medicinal plants; signal transduction.
Figures


References
-
- Mahata S, Pandey A, Shukla S, Tyagi A, Husain SA, Das BC, Bharti AC. Anticancer activity of Phyllanthus emblica Linn. (Indian gooseberry): Inhibition of transcription factor AP-1 and HPV gene expression in cervical cancer cells. Nutr Cancer. 2013;65:S88–S97. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2013.785008. (Suppl) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
