Hepatectomy combined with microwave ablation of the spleen for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma complicated with splenomegaly: A retrospective study
- PMID: 28357095
- PMCID: PMC5351759
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2016.1111
Hepatectomy combined with microwave ablation of the spleen for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma complicated with splenomegaly: A retrospective study
Abstract
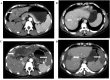
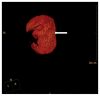
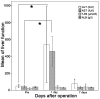
The present retrospective study aimed to investigate the mid-term safety and efficacy of hepatectomy combined with microwave ablation of the partial spleen for treatment of liver cancer complicated with hypersplenism. A retrospective analysis was performed on 23 patients who underwent hepatectomy combined with microwave ablation of the partial spleen for liver cancer, complicated with hypersplenism that was secondary to cirrhosis. The splenic and ablated volumes were calculated according to a contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan prior to and 2 weeks after the operation. Complete blood count and liver function tests were examined prior to and following the surgery, and complications and changes in the blood tests were monitored for 6 months. Over this period of investigation, the splenic volume was reduced by a mean value of 34.0%. The levels of serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase were increased on the first day after the operation (P<0.05), although they recovered to the normal level within 1 week (P<0.05). The total level of bilirubin increased slightly, along with moderately decreased levels of albumin and cholinesterase on the first day, although these changes were not significant compared with the baseline (P>0.05). The white blood cell count was persistently significantly higher compared with the baseline over the course of the 6 months (P>0.05). The platelet count did not increase significantly for the first week after the operation (P>0.05); however, it was revealed to be significantly increased 1 month after the surgery (P<0.05). No significant complications were occurred during the follow-up period. In conclusion, hepatectomy combined with microwave ablation of the spleen was demonstrated to be a safe and effective procedure for patients with liver cancer and hypersplenism in the mid-term.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; hypersplenism; microwave ablation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Microwave ablation in the spleen for treatment of secondary hypersplenism: a preliminary study.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011 Mar;196(3):692-6. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.4193. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011. PMID: 21343515
-
[Role of united hepatectomy and splenectomy in the surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma complicated with hepatic cirrhosis and hypersplenism].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2005 Apr 1;43(7):442-6. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15854370 Chinese.
-
Percutaneous Microwave Ablation in the Spleen for Treatment of Hypersplenism in Cirrhosis Patients.Dig Dis Sci. 2016 Jan;61(1):287-92. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3732-7. Epub 2015 Jun 2. Dig Dis Sci. 2016. PMID: 26031423 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma and secondary hypersplenism.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2006 Aug;5(3):396-400. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2006. PMID: 16911938
-
Thermal ablation for partial splenectomy hemostasis, spleen trauma, splenic metastasis and hypersplenism.Hepatogastroenterology. 2013 May;60(123):501-6. doi: 10.5754/hge12853. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23159352 Review.
Cited by
-
Microwave hyperthermia promotes caspase‑3-dependent apoptosis and induces G2/M checkpoint arrest via the ATM pathway in non‑small cell lung cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2018 Aug;53(2):539-550. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4439. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29901106 Free PMC article.
-
[Microwave Hyperthermia Combined with Gemcitabine Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Lung Squamous Carcinoma Cells].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018 Nov 20;21(11):805-814. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2018.11.01. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30454541 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Nanashima A, Abo T, Takeshita H, Yamasaki N, Sawai T, Nagayasu T. Safety of hepatectomy accompanying combined resection of other organs. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012;59:1915–1920. - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Li C, Wen TF, Yan LN, Li B, Liang GL, Li KW. Safety of synchronous hepatectomy and splenectomy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and hypersplenism. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012;59:526–528. - PubMed
-
- Aiyama T, Kamiyama T, Nakanishi K, Yokoo H, Taniguchi M, Fukumori D, Tahara M, Kakisaka T, Kamachi H, Matsushita M, Todo S. A study of cirrhotic patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and huge splenomegaly who received treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with concomitant splenectomy. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2010;37:2683–2686. (In Japanese) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
