Influence of age on intestinal bile acid transport in C57BL/6 mice
- PMID: 28357119
- PMCID: PMC5368957
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.287
Influence of age on intestinal bile acid transport in C57BL/6 mice
Abstract
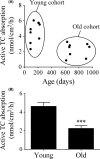
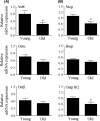
Intestinal and hepatic bile acid transporters are important for enterohepatic bile acid circulation and pharmacokinetics. Based on previous literature, we hypothesized that the expression of bile acid transporters and intestinal bile acid absorption are lower in older individuals. Here, we measured active taurocholate absorption across the ileum of male C57BL/6 mice in two different age cohorts - young (age range of 89-224 days) and old (age range of 613-953 days). Also examined in these mice were mRNA expression of the major bile acid transporters - Asbt and Ostα/β in the ileum, and Ntcp, Oatp1b2 and Bsep in the liver. Mean intestinal taurocholate absorption was significantly lower (~50%) in mice in the older cohort compared to those in the younger cohort. In the ileum, the expression of Asbt was significantly lower in the older cohort, but expression of Ostα/β was not affected by age. The lower capacity for intestinal bile acid absorption in the older animals is consistent with their lower expression level of Asbt. Of the hepatic bile acid transporters examined, expression of Ntcp and Oatp1b2 were significantly lower in the older mice. This is the first study to directly measure intestinal bile acid absorption as a function of age. The data suggest a lower capacity for intestinal bile acid absorption in older animals. Also, lower expression of Asbt, Ntcp, and Oatp1b2 in older individuals could influence pharmacokinetics of drug substrates.
Keywords: Age; Ussing chambers; bile acid; bile acid transporters; intestine; liver.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The influences of cholecystectomy on the circadian rhythms of bile acids as well as the enterohepatic transporters and enzymes systems in mice.Chronobiol Int. 2018 May;35(5):673-690. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2018.1426596. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Chronobiol Int. 2018. PMID: 29381405
-
n-3 Fatty Acids Abrogate Dyslipidemia-Induced Changes in Bile Acid Uptake, Synthesis, and Transport in Young and Aged Dyslipidemic Rats.Lipids. 2019 Jan;54(1):39-51. doi: 10.1002/lipd.12125. Epub 2019 Feb 10. Lipids. 2019. PMID: 30740707
-
Weanling, but not adult, rabbit colon absorbs bile acids: flux is linked to expression of putative bile acid transporters.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006 Mar;290(3):G439-50. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00163.2005. Epub 2005 Sep 15. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16166347
-
Bile acid transporters: structure, function, regulation and pathophysiological implications.Pharm Res. 2007 Oct;24(10):1803-23. doi: 10.1007/s11095-007-9289-1. Epub 2007 Apr 3. Pharm Res. 2007. PMID: 17404808 Review.
-
The solute carrier family SLC10: more than a family of bile acid transporters regarding function and phylogenetic relationships.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2006 Mar;372(6):413-31. doi: 10.1007/s00210-006-0043-8. Epub 2006 Mar 16. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16541252 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of dietary pectin on the profile and transport of intestinal bile acids in young pigs.J Anim Sci. 2018 Nov 21;96(11):4743-4754. doi: 10.1093/jas/sky327. J Anim Sci. 2018. PMID: 30102377 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Absorption of Bile Acids in Health and Disease.Compr Physiol. 2019 Dec 18;10(1):21-56. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c190007. Compr Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31853951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased intestinal bile acid absorption contributes to age-related cognitive impairment.Cell Rep Med. 2024 May 21;5(5):101543. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101543. Epub 2024 May 1. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 38697101 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Lipid Metabolism in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Diseases in the Elderly.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 3;15(15):3433. doi: 10.3390/nu15153433. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37571370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Profiling of Bile Acids in Feces of Humans and Rodents by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry.Metabolites. 2022 Jul 11;12(7):633. doi: 10.3390/metabo12070633. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35888757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen L, Yao X, Young A, McNulty J, Anderson D, Liu Y, et al. (2012). Inhibition of apical sodium‐dependent bile acid transporter as a novel treatment for diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 302: E68–E76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

