A Rapid Biochemical and Radiological Response to the Concomitant Therapy with Temozolomide and Radiotherapy in an Aggressive ACTH Pituitary Adenoma
- PMID: 28357143
- PMCID: PMC5357528
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/2419590
A Rapid Biochemical and Radiological Response to the Concomitant Therapy with Temozolomide and Radiotherapy in an Aggressive ACTH Pituitary Adenoma
Abstract
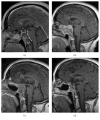
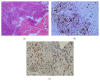
Background and Importance. In the last eight years temozolomide (TMZ) has been used as the last-line treatment modality for aggressive pituitary tumors to be applied after the failure of surgery, medical therapy, and radiotherapy. The objective was to achieve a rapid control of tumor growth and hormone normalization with concurrent chemoradiotherapy in a patient with very aggressive ACTH pituitary adenoma. Clinical Presentation. We describe a patient with an aggressive ACTH-producing adenoma treated with concurrent temozolomide and radiotherapy. The patient suffered from an aggressive ACTH adenoma resistant to surgical and medical treatment. After two months of concurrent temozolomide and radiotherapy, cortisol normalization and significant tumor shrinkage were observed. After 22 months of follow-up, there is still no evidence of tumor recurrence. Conclusion. Concurrent treatment with temozolomide and irradiation appears to be highly effective in the achievement of the tumor volume control as well as in the control of ACTH secretion in aggressive ACTH adenoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bush Z. M., Longtine J. A., Cunningham T., et al. Temozolomide treatment for aggressive pituitary tumors: correlation of clinical outcome with O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation and expression. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2010;95(11):E280–E290. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0441. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

