Lesch-Nyhan syndrome: The saga of metabolic abnormalities and self-injurious behavior
- PMID: 28357186
- PMCID: PMC5359358
- DOI: 10.5582/irdr.2016.01076
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome: The saga of metabolic abnormalities and self-injurious behavior
Abstract
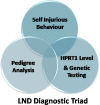
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome (LNS) is an X-linked recessive disorder of purine metabolism caused by a mutation in Xq26.2-q26.3 (OMIM 308000.0004). The presence of the diagnostic triad, i.e. signs of self-injurious behavior (SIB) and results of pedigree analysis and novel molecular biology & genetic testing, confirms the diagnosis of LNS. With a level of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl-transferase 1 (HPRT1) enzyme activity < 2%, patients develop neurological, neurocognitive, and neuromotor symptoms along with SIB. Described here is a case of 4-year-old boy who was diagnosed with LNS. The boy displayed SIB, i.e. biting of the lips and fingers, and he had cerebral venous sinus thrombosis caused by LNS.
Keywords: Lesch-Nyhan disease; X-linked disorder; self-injurious behavior.
Figures


References
-
- Lesch M, Nyhan WL. A familial disorder of uric acid metabolism and central nervous system function. Am J Med. 1964; 36:561-570. - PubMed
-
- Cauwels RG, Martens LC. Self-mutilation behaviour in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. J Oral Pathol Med. 2005; 34:573-575. - PubMed
-
- Robey KL, Reck JF, Giacomini KD, Barabas G, Eddey GE. Modes and patterns of self-mutilation in persons with Lesch-Nyhan disease. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2003; 45:167-171. - PubMed
-
- Limeres J, Feijoo JF, Baluja F, Seoane JM, Diniz M, Diz P. Oral self-injury: An update. Dent Traumatol. 2013; 29:8-14. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
