Towards understanding the gliotoxin detoxification mechanism: in vivo thiomethylation protects yeast from gliotoxin cytotoxicity
- PMID: 28357342
- PMCID: PMC5349022
- DOI: 10.15698/mic2016.03.485
Towards understanding the gliotoxin detoxification mechanism: in vivo thiomethylation protects yeast from gliotoxin cytotoxicity
Abstract
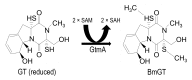
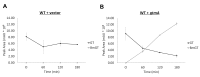
Gliotoxin (GT) is a mycotoxin produced by some species of ascomycete fungi including the opportunistic human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. In order to produce GT the host organism needs to have evolved a self-protection mechanism. GT contains a redox-cycling disulfide bridge that is important in mediating toxicity. Recently is has been demonstrated that A. fumigatus possesses a novel thiomethyltransferase protein called GtmA that has the ability to thiomethylate GT in vivo, which aids the organism in regulating GT biosynthesis. It has been suggested that thiomethylation of GT and similar sulfur-containing toxins may play a role in providing self-protection in host organisms. In this work we have engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a GT-naïve organism, to express A. fumigatus GtmA. We demonstrate that GtmA can readily thiomethylate GT in yeast, which results in protection of the organism from exogenous GT. Our work has implications for understanding the evolution of GT self-protection mechanisms in organisms that are GT producers and non-producers.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; gliotoxin; oxidoreductase GliT; thio-methyltransferase GtmA.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no existing conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural, mechanistic and functional insight into gliotoxin bis-thiomethylation in Aspergillus fumigatus.Open Biol. 2017 Feb;7(2):160292. doi: 10.1098/rsob.160292. Open Biol. 2017. PMID: 28179499 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Sulfur in the Biosynthesis of Essential Metabolites in Pathogenic Fungi of Animals, Particularly Aspergillus spp.: Molecular and Therapeutic Implications.Front Microbiol. 2019 Dec 13;10:2859. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02859. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31921039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of gliotoxin biosynthesis and protection in Aspergillus species.PLoS Genet. 2022 Jan 18;18(1):e1009965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009965. eCollection 2022 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35041649 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of nonribosomal peptide synthesis: bis-thiomethylation attenuates gliotoxin biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus.Chem Biol. 2014 Aug 14;21(8):999-1012. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.07.006. Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 25126990
-
Biosynthesis and function of gliotoxin in Aspergillus fumigatus.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Jan;93(2):467-72. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3689-1. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22094977 Review.
Cited by
-
The Metabolite Profiling of Aspergillus fumigatus KMM4631 and Its Co-Cultures with Other Marine Fungi.Metabolites. 2023 Nov 8;13(11):1138. doi: 10.3390/metabo13111138. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37999234 Free PMC article.
-
Structural, mechanistic and functional insight into gliotoxin bis-thiomethylation in Aspergillus fumigatus.Open Biol. 2017 Feb;7(2):160292. doi: 10.1098/rsob.160292. Open Biol. 2017. PMID: 28179499 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus mitogen-activated protein kinase MpkA is involved in gliotoxin production and self-protection.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 2;15(1):33. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44329-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38167253 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Sulfur in the Biosynthesis of Essential Metabolites in Pathogenic Fungi of Animals, Particularly Aspergillus spp.: Molecular and Therapeutic Implications.Front Microbiol. 2019 Dec 13;10:2859. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02859. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31921039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of gliotoxin biosynthesis and protection in Aspergillus species.PLoS Genet. 2022 Jan 18;18(1):e1009965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009965. eCollection 2022 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35041649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson JR, Bruce WF, Dutcher JD. Gliotoxin, The Antibiotic Principle of Gliocladium fimbriatum. I. Production, Physical and Biological Properties 1. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1943;65(10):2005–2009. doi: 10.1021/ja01250a051. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
