Advancing host-directed therapy for tuberculosis
- PMID: 28357397
- PMCID: PMC5349197
- DOI: 10.15698/mic2017.03.565
Advancing host-directed therapy for tuberculosis
Abstract
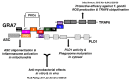
Tuberculosis (TB) drug-development strategies, a wide range of candidate host-directed therapies (HDT)s-including new and repurposed drugs, biologics, and cellular therapies-have been proposed to accelerate eradication of infection and overcome the problems associated with current treatment regimens. By investigating the interaction between macrophages and the intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii), we uncovered that infection-induced signaling pathways suggest possibilities for the development of novel therapeutic modalities for TB that target the intracellular signaling pathways permitting the replication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB).
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Toxoplasma gondii GRA7; macrophages; protein-protein interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment on
-
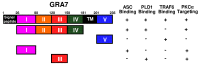
Toxoplasma gondii GRA7-Targeted ASC and PLD1 Promote Antibacterial Host Defense via PKCα.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jan 26;13(1):e1006126. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006126. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28125719 Free PMC article.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
