FUS affects circular RNA expression in murine embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons
- PMID: 28358055
- PMCID: PMC5379105
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14741
FUS affects circular RNA expression in murine embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons
Abstract
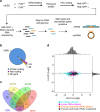
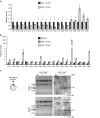
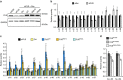
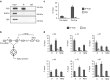
The RNA-binding protein FUS participates in several RNA biosynthetic processes and has been linked to the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia. Here we report that FUS controls back-splicing reactions leading to circular RNA (circRNA) production. We identified circRNAs expressed in in vitro-derived mouse motor neurons (MNs) and determined that the production of a considerable number of these circRNAs is regulated by FUS. Using RNAi and overexpression of wild-type and ALS-associated FUS mutants, we directly correlate the modulation of circRNA biogenesis with alteration of FUS nuclear levels and with putative toxic gain of function activities. We also demonstrate that FUS regulates circRNA biogenesis by binding the introns flanking the back-splicing junctions and that this control can be reproduced with artificial constructs. Most circRNAs are conserved in humans and specific ones are deregulated in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived MNs carrying the FUSP525L mutation associated with ALS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Commentary: FUS affects circular RNA expression in murine embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Dec 12;10:412. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00412. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29311805 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

