MiRNA199a-3p suppresses tumor growth, migration, invasion and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting VEGFA, VEGFR1, VEGFR2, HGF and MMP2
- PMID: 28358369
- PMCID: PMC5386529
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2017.123
MiRNA199a-3p suppresses tumor growth, migration, invasion and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting VEGFA, VEGFR1, VEGFR2, HGF and MMP2
Abstract
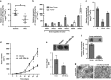
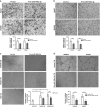
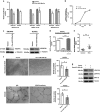
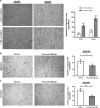
Increasing significance of tumor-stromal interaction in development and progression of cancer implies that signaling molecules in the tumor microenvironment (TME) might be the effective therapeutic targets for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, the role of microRNA miR-199a-3p in the regulation of TME and development of HCC has been investigated by several in vitro and in vivo assays. Expression of miR-199a-3p was observed significantly low in HCC tissues and its overexpression remarkably inhibited in vivo tumor growth and metastasis to lung in NOD-SCID mice. In vitro restoration of miR-199a-3p expression either in endothelial cells (ECs) or in cancer cells (CACs) significantly diminished migration of ECs in co-culture assay. Again incubation of miR-199a-3p transfected ECs with either conditioned media (CM) of CACs or recombinant VEGF has reduced tube formation, in ECs and it was also dropped upon growth in CM of either anti-VEGF antibody-treated or miR-199a-3p-transfected CACs. In addition, bioinformatics and luciferase-reporter assays revealed that miR-199a-3p inhibited VEGF secretion from CACs and VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 expression on ECs and thus restricted cross talk between CACs and ECs. Again, restoration of miR-199a-3p in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) reduced migration and invasion of CACs in co-culture assay, while it was enhanced by the overexpression of HGF suggesting miR-199a-3p has hindered HSC-CACs cross talk probably by inhibiting HGF and regulating matrix metalloproteinase MMP2, which were found as targets of miR-199a-3p subsequently by luciferase-reporter assay and gelatin zymography, respectively. Thus, these findings collectively highlight that miR-199a-3p restricts metastasis, invasion and angiogenesis in HCC and hence it may be considered as one of the powerful effective therapeutics for management of HCC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
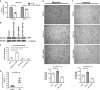
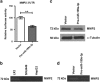
Similar articles
-
miR-142-3p Inhibits the Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Regulating HMGB1 Gene Expression.Curr Mol Med. 2018;18(3):135-141. doi: 10.2174/1566524018666180907161124. Curr Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30198432
-
Anti-invasion and anti-migration effects of miR-199a-3p in hepatocellular carcinoma are due in part to targeting CD151.Int J Oncol. 2016 Nov;49(5):2037-2045. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3677. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27599545
-
Down-regulation of microRNA-338-3p promoted angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:583-591. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.056. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27694002
-
Updates on the hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met axis in hepatocellular carcinoma and its therapeutic implications.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Sep 7;24(33):3695-3708. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i33.3695. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30197476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Endoglin (CD105) in the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 5;19(12):3887. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123887. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30563158 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the multifaceted role of microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Integrating literature review and bioinformatics analysis for therapeutic insights.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 18;10(20):e39489. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39489. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39498055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-199a-5p promotes the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells by increasing AKAP1 expression.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jun;21(6):434. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12695. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33868472 Free PMC article.
-
miR‑140‑5p regulates cell migration and invasion of non‑small cell lung cancer cells through targeting VEGFA.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Sep;18(3):2866-2872. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9291. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30015904 Free PMC article.
-
Houshiheisan promotes angiogenesis via HIF-1α/VEGF and SDF-1/CXCR4 pathways: in vivo and in vitro.Biosci Rep. 2019 Oct 30;39(10):BSR20191006. doi: 10.1042/BSR20191006. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31652450 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-126 negatively regulates PLK-4 to impact the development of hepatocellular carcinoma via ATR/CHEK1 pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Oct 12;9(10):1045. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1020-0. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30315225 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

