Novel prosurvival function of Yip1A in human cervical cancer cells: constitutive activation of the IRE1 and PERK pathways of the unfolded protein response
- PMID: 28358375
- PMCID: PMC5386543
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2017.147
Novel prosurvival function of Yip1A in human cervical cancer cells: constitutive activation of the IRE1 and PERK pathways of the unfolded protein response
Abstract
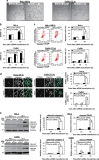
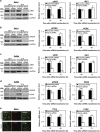
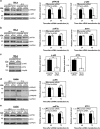
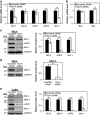
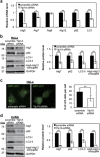
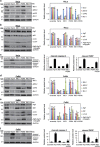
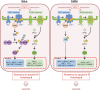
Cancer cells are under chronic endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress due to hypoxia, low levels of nutrients, and a high metabolic demand for proliferation. To survive, they constitutively activate the unfolded protein response (UPR). The inositol-requiring protein 1 (IRE1) and protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase (PERK) signaling branches of the UPR have been shown to have cytoprotective roles in cancer cells. UPR-induced autophagy is another prosurvival strategy of cancer cells, possibly to remove misfolded proteins and supply nutrients. However, the mechanisms by which cancer cells exploit the UPR and autophagy machinery to promote survival and the molecules that are essential for these processes remain to be elucidated. Recently, a multipass membrane protein, Yip1A, was shown to function in the activation of IRE1 and in UPR-induced autophagy. In the present study, we explored the possible role of Yip1A in activation of the UPR by cancer cells for their survival, and found that depletion of Yip1A by RNA interference (RNAi) induced apoptotic cell death in HeLa and CaSki cervical cancer cells. Intriguingly, Yip1A was found to activate the IRE1 and PERK pathways of the UPR constitutively in HeLa and CaSki cells. Yip1A mediated the phosphorylation of IRE1 and also engaged in the transcription of PERK. The activation of these signaling pathways upregulated the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins and autophagy-related proteins. These events might enhance resistance to apoptosis and promote cytoprotective autophagy in HeLa and CaSki cells. The present study is the first to uncover a key prosurvival modulator, Yip1A, which coordinates IRE1 signaling with PERK signaling to support the survival of HeLa and CaSki cervical cancer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ma Y, Hendershot LM. The role of the unfolded protein response in tumour development: friend or foe? Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 966–977. - PubMed
-
- Moenner M, Pluquet O, Bouchecareilh M, Chevet E. Integrated endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in cancer. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 10631–10634. - PubMed
-
- Wang M, Kaufman RJ. The impact of the endoplasmic reticulum protein-folding environment on cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 2014; 14: 581–597. - PubMed
-
- Nagelkerke A, Bussink J, FCGJ Sweep, Span PN. The unfolded protein response as a target for cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014; 1846: 277–284. - PubMed
-
- Walter P, Ron D. The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 2011; 334: 1081–1086. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

