Attenuation of UV-B exposure-induced inflammation by abalone hypobranchial gland and gill extracts
- PMID: 28358420
- PMCID: PMC5403342
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2939
Attenuation of UV-B exposure-induced inflammation by abalone hypobranchial gland and gill extracts
Abstract
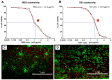
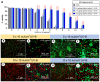
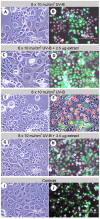
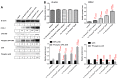
Exposure to solar ultraviolet B (UV-B) is a known causative factor for many skin complications such as wrinkles, black spots, shedding and inflammation. Within the wavelengths 280‑320 nm, UV-B can penetrate to the epidermal level. This investigation aimed to test whether extracts from the tropical abalone [Haliotis asinina (H. asinina)] mucus-secreting tissues, the hypobranchial gland (HBG) and gills, were able to attenuate the inflammatory process, using the human keratinocyte HaCaT cell line. Cytotoxicity of abalone tissue extracts was determined using an AlamarBlue viability assay. Results showed that HaCaT cells could survive when incubated in crude HBG and gill extracts at concentrations between <11.8 and <16.9 µg/ml, respectively. Subsequently, cell viability was compared between cultured HaCaT cells exposed to serial doses of UV-B from 1 to 11 (x10) mJ/cm2 and containing 4 different concentrations of abalone extract from both the HBG and gill (0, 0.1, 2.5, 5 µg/ml). A significant increase in cell viability was observed (P<0.001) following treatment with 2.5 and 5 µg/ml extract. Without extract, cell viability was significantly reduced upon exposure to UV-B at 4 mJ/cm2. Three morphological changes were observed in HaCaT cells following UV-B exposure, including i) condensation of cytoplasm; ii) shrunken cells and plasma membrane bubbling; and iii) condensation of chromatin material. A calcein AM‑propidium iodide live‑dead assay showed that cells could survive cytoplasmic condensation, yet cell death occurred when damage also included membrane bubbling and chromatin changes. Western blot analysis of HaCaT cell COX‑2, p38, phospho‑p38, SPK/JNK and phospho‑SPK/JNK following exposure to >2.5 µg/ml extract showed a significant decrease in intensity for COX‑2, phospho‑p38 and phospho‑SPK/JNK. The present study demonstrated that abalone extracts from the HGB and gill can attenuate inflammatory proteins triggered by UV-B. Hence, the contents of abalone extract, including cellmetabolites and peptides, may provide new agents for skin anti‑inflammation, preventing damage due to UV-B.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic phototoxic effects of glycolic acid in a human keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT).J Dermatol Sci. 2011 Dec;64(3):191-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2011.09.001. Epub 2011 Sep 24. J Dermatol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21993420
-
Myricetin protects keratinocyte damage induced by UV through IκB/NFκb signaling pathway.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2017 Dec;16(4):444-449. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12399. Epub 2017 Aug 17. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28834104
-
A comparative study of UV-induced cell signalling pathways in human keratinocyte-derived cell lines.Arch Dermatol Res. 2013 Nov;305(9):817-33. doi: 10.1007/s00403-013-1412-z. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Arch Dermatol Res. 2013. PMID: 24071771
-
Protective effect of ixerisoside A against UVB-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine production in human keratinocytes.Int J Mol Med. 2015 May;35(5):1411-8. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2120. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25738262
-
Pomegranate fruit extract modulates UV-B-mediated phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and activation of nuclear factor kappa B in normal human epidermal keratinocytes paragraph sign.Photochem Photobiol. 2005 Jan-Feb;81(1):38-45. doi: 10.1562/2004-08-06-RA-264. Photochem Photobiol. 2005. PMID: 15493960
Cited by
-
1,2-Bis[(3-Methoxyphenyl)Methyl]Ethane-1,2-Dicarboxylic Acid Reduces UVB-Induced Photodamage In Vitro and In Vivo.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Oct 5;8(10):452. doi: 10.3390/antiox8100452. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31590372 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-Aided Virtual Screening and In Vitro Validation of Biomimetic Tyrosinase Inhibitory Peptides from Abalone Peptidome.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 5;24(4):3154. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043154. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834568 Free PMC article.
-
Keratinocyte Growth Factor 2 Ameliorates UVB-Induced Skin Damage via Activating the AhR/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 7;12:655281. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.655281. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34163354 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Sesamin against UVB-Induced Skin Inflammation and Photodamage In Vitro and In Vivo.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 12;9(9):479. doi: 10.3390/biom9090479. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31547364 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

