Circulating microRNA-194 regulates human melanoma cells via PI3K/AKT/FoxO3a and p53/p21 signaling pathway
- PMID: 28358423
- PMCID: PMC5428795
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2017.5537
Circulating microRNA-194 regulates human melanoma cells via PI3K/AKT/FoxO3a and p53/p21 signaling pathway
Abstract
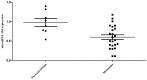
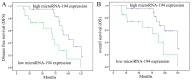
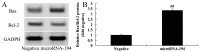
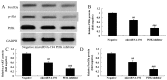
In the present study, we analyzed the role of microRNA-194 circulating regulated human melanoma cell growth. We found that microRNA-194 expression was markedly suppressed in human melanoma patients, compared with negative control group. Next, disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) of high expression in human melanoma patients was higher than those of low expression in human melanoma patients. MicroRNA-194 overexpression inhibited cell proliferation, induced apoptosis, increased caspase-3/-9 activities and promoted Bax/Bcl-2 of human melanoma cells. Furthermore, microRNA-194 overexpression also suppressed PI3K/AKT/FoxO3a signaling pathway and induced p53/p21 signaling pathway. PI3K inhibitor, suppressed PI3K, phosphorylation-AKT, FoxO3a protein expression and increased the effects of microRNA-194 overexpression on cell growth, apoptosis, caspase-3/-9 activities and Bax/Bcl-2 protein expression of human melanoma cells through the induction of p53/p21 signaling pathway. Taken together, these data indicate that circulating microRNA-194 regulated human melanoma cells via PI3K/AKT/FoxO3a and p53/p21 signaling pathway.
Figures

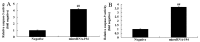


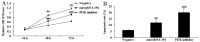
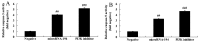


Similar articles
-
Anti-microRNA-132 causes sevoflurane‑induced neuronal apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT/FOXO3a pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Dec;42(6):3238-3246. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3895. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30272258 Free PMC article.
-
Pristimerin-induced uveal melanoma cell death via inhibiting PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jun;24(11):6208-6219. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15249. Epub 2020 Apr 29. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32347651 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-125b regulates apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer via the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2017 Sep;38(3):1715-1723. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5808. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28713974
-
Mechanism of the inhibition of leukemia cell growth and induction of apoptosis through the activation of ATR and PTEN by the topoisomerase inhibitor 3EZ, 20Ac-ingenol.Leuk Res. 2015 Sep;39(9):927-32. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2015.06.006. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Leuk Res. 2015. PMID: 26194899 Review.
-
The Akt-associated microRNAs.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Nov;69(21):3601-12. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1129-8. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22936352 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating miR-320a Acts as a Tumor Suppressor and Prognostic Factor in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 23;11:645475. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.645475. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33833996 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of BMI1 Gene on Regulating Apoptosis, Invasion, and Migration of HEC-1B Cells Induced by Ionizing Radiation.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Mar 2;2022:7052066. doi: 10.1155/2022/7052066. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9804590. doi: 10.1155/2023/9804590. PMID: 35281533 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
MicroRNA Signature in Melanoma: Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 22;11:608987. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.608987. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33968718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between small and long non-coding RNAs in cutaneous melanoma: a complex jigsaw puzzle with missing pieces.Mol Oncol. 2019 Jan;13(1):74-98. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12412. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Mol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30499222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Down-regulation of miR-543 expression increases the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to 5-Fluorouracil through the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway.Biosci Rep. 2019 Mar 22;39(3):BSR20190249. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190249. Print 2019 Mar 29. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30842340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greene JM, Schneble EJ, Jackson DO, Hale DF, Vreeland TJ, Flores M, Martin J, Herbert GS, Hardin MO, Yu X, et al. A phase I/IIa clinical trial in stage IV melanoma of an autologous tumor-dendritic cell fusion (dendritoma) vaccine with low dose interleukin-2. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2016;65:383–392. doi: 10.1007/s00262-016-1809-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eggermont AM, Suciu S, Rutkowski P, Kruit WH, Punt CJ, Dummer R, Salès F, Keilholz U, de Schaetzen G, Testori A. EORTC Melanoma Group: Long term follow up of the EORTC 18952 trial of adjuvant therapy in resected stage IIB-III cutaneous melanoma patients comparing intermediate doses of interferon-alpha-2b (IFN) with observation: Ulceration of primary is key determinant for IFN-sensitivity. Eur J Cancer. 2016;55:111–121. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.11.014. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

