Sclerotherapy for Orbital Lymphangioma - Case Series and Literature Review
- PMID: 28358710
- PMCID: PMC5411755
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11055
Sclerotherapy for Orbital Lymphangioma - Case Series and Literature Review
Abstract
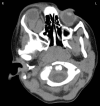
Orbital lymphangioma is a lymphatic system lesion that commonly presents in childhood. Management of these lesions is complex. Sclerotherapy is a therapy used to treat and shrink lesions prior to or as an alternative to surgery. We present three cases of orbital lymphangioma that were treated with sclerotherapy. Case 1: A 6-month-old boy was presented in 2010 with right ptosis and proptosis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) identified a lesion involving the right orbit and face. Case 2: A 3-year-old girl was presented in 2011 with intermittent right periorbital swelling and medial canthal bleeding. MRI identified a soft-tissue lesion in the right orbit, extending into the face. Case 3: A 3-year-old girl was presented in 2012 with vomiting, and painful right proptosis. MRI identified an intra-conal lesion in the right orbit with fluid filled levels. All three patients were treated with sclerotherapy (sodium tetradecylsulfate). Sclerotherapy is a promising treatment for orbital lymphangioma. Its use may prevent the need for, or minimise the amount of surgical management. Several sclerosants are now commonly used to treat these lesions.
Keywords: Paediatric; lymphangioma; orbital; sclerotherapy; sodium tetradecylsulfate (STS).
Copyright© 2017, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Harris GJ, Sakol PJ, Bonavolontà G, De Conciliis C. An analysis of thirty cases of orbital lymphangioma. Pathophysiologic considerations and management recommendations. Ophthalmology. 1990;97(12):1583–1592. - PubMed
-
- Iliff WJ, Green WR. Orbital lymphangiomas. Ophthalmology. 1979;86(5):914–929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
