Intracellular HIV-1 RNA and CD4+ T-cell activation in patients starting antiretrovirals
- PMID: 28358734
- PMCID: PMC5572749
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001480
Intracellular HIV-1 RNA and CD4+ T-cell activation in patients starting antiretrovirals
Abstract
Objective: To assess if the reduction in HIV-1 RNA in CD4 T cells is correlated with the persistence of immune activation following early antiretroviral therapy (ART).
Design: Clinical trial (NCT01285050).
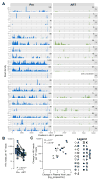
Methods: Next-generation sequencing was used to study total RNA from activated CD4 T cells (CD38 and human leukocyte antigen - antigen D related (HLA-DR) expressing) collected from 19 treatment-naïve HIV-1/hepatitis C virus-infected patients before and early after ART initiation (≥12 weeks after plasma HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/ml). To validate comparisons, pre and post-ART measures were adjusted for input RNA and overall read number.
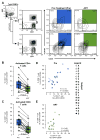
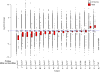
Results: As expected, ART use was associated with a median [interquartile range (IQR)] 4.3% (2.2-8.3) reduction in the proportion of activated CD4 T cells (P = 0.0008). Whereas in those activated CD4 T cells no consistent differences in overall gene expression were detected, interferon-stimulated gene expression declined (P < 2 × 10). Pre-ART, sorted activated CD4 T cells contained a median (IQR) of 959 (252-1614) HIV-1 reads/10 reads compared with 72 (55-152) HIV-1 reads/10 reads after at least 12 weeks of suppressive ART (P = 8 × 10). The decrease in HIV-1 reads in activated CD4 T cells was associated with the change in plasma HIV-1 RNA levels (r = 0.77, P = 2 × 10) and the change in the proportion of activated CD4 T cells (r = 0.70, P = 0.0016).
Conclusion: Months of ART led to a marked decrease in cell-associated HIV-1 RNA and interferon-stimulated genes expression in activated CD4 T cells that were strongly associated with the reduction in the proportion of activated CD4 T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
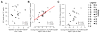
References
-
- Warriner AH, Burkholder GA, Overton ET. HIV-related metabolic comorbidities in the current ART era. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2014;28:457–476. - PubMed
-
- Aounallah M, Dagenais-Lussier X, El-Far M, Mehraj V, Jenabian MA, Routy JP, et al. Current topics in HIV pathogenesis, part 2: Inflammation drives a Warburg-like effect on the metabolism of HIV-infected subjects. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016;28:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

