Pharmacological interventions for non-alcohol related fatty liver disease (NAFLD): an attempted network meta-analysis
- PMID: 28358980
- PMCID: PMC6464620
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011640.pub2
Pharmacological interventions for non-alcohol related fatty liver disease (NAFLD): an attempted network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Non-alcohol related fatty liver disease (commonly called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)) is liver steatosis in the absence of significant alcohol consumption, use of hepatotoxic medication, or other disorders affecting the liver such as hepatitis C virus infection, Wilson's disease, and starvation. NAFLD embraces the full spectrum of disease from pure steatosis (i.e. uncomplicated fatty liver) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), via NASH-cirrhosis to cirrhosis. The optimal pharmacological treatment for people with NAFLD remains uncertain.
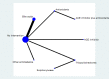
Objectives: To assess the comparative benefits and harms of different pharmacological interventions in the treatment of NAFLD through a network meta-analysis and to generate rankings of the available pharmacological treatments according to their safety and efficacy. However, it was not possible to assess whether the potential effect modifiers were similar across different comparisons. Therefore, we did not perform the network meta-analysis, and instead, assessed the comparative benefits and harms of different interventions using standard Cochrane methodology.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, Embase, Science Citation Index Expanded, the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, and ClinicalTrials.com to August 2016.
Selection criteria: We included only randomised clinical trials (irrespective of language, blinding, or publication status) in participants with NAFLD. We excluded trials which included participants who had previously undergone liver transplantation. We considered any of the various pharmacological interventions compared with each other or with placebo or no intervention.
Data collection and analysis: We calculated the odds ratio (OR) and rate ratio with 95% confidence intervals (CI) using both fixed-effect and random-effects models based on an available participant analysis with Review Manager. We assessed risk of bias according to the Cochrane risk of bias tool, controlled risk of random errors with Trial Sequential Analysis, and assessed the quality of the evidence using GRADE.
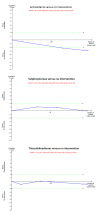
Main results: We identified 77 trials including 6287 participants that met the inclusion criteria of this review. Forty-one trials (3829 participants) provided information for one or more outcomes. Only one trial was at low risk of bias in all domains. All other trials were at high risk of bias in one or more domains. Overall, all the evidence was very low quality. Thirty-five trials included only participants with non-alcohol related steatohepatitis (NASH) (based on biopsy confirmation). Five trials included only participants with diabetes mellitus; 14 trials included only participants without diabetes mellitus. The follow-up in the trials ranged from one month to 24 months.We present here only the comparisons of active intervention versus no intervention in which two or more trials reported at least one of the following outcomes: mortality at maximal follow-up, serious adverse events, and health-related quality of life, the outcomes that determine whether a treatment should be used. Antioxidants versus no interventionThere was no mortality in either group (87 participants; 1 trial; very low quality evidence). None of the participants developed serious adverse events in the trial which reported the proportion of people with serious adverse events (87 participants; 1 trial; very low quality evidence). There was no evidence of difference in the number of serious adverse events between antioxidants and no intervention (rate ratio 0.89, 95% CI 0.36 to 2.19; 254 participants; 2 trials; very low quality evidence). None of the trials reported health-related quality of life. Bile acids versus no interventionThere was no evidence of difference in mortality at maximal follow-up (OR 5.11, 95% CI 0.24 to 107.34; 659 participants; 4 trials; very low quality evidence), proportion of people with serious adverse events (OR 1.56, 95% CI 0.84 to 2.88; 404 participants; 3 trials; very low quality evidence), or the number of serious adverse events (rate ratio 1.01, 95% CI 0.66 to 1.54; 404 participants; 3 trials; very low quality evidence) between bile acids and no intervention. None of the trials reported health-related quality of life. Thiazolidinediones versus no interventionThere was no mortality in either group (74 participants; 1 trial; very low quality evidence). None of the participants developed serious adverse events in the two trials which reported the proportion of people with serious adverse events (194 participants; 2 trials; very low quality evidence). There was no evidence of difference in the number of serious adverse events between thiazolidinediones and no intervention (rate ratio 0.25, 95% CI 0.06 to 1.05; 357 participants; 3 trials; very low quality evidence). None of the trials reported health-related quality of life. Source of fundingTwenty-six trials were partially- or fully-funded by pharmaceutical companies that would benefit, based on the results of the trial. Twelve trials did not receive any additional funding or were funded by parties with no vested interest in the results. The source of funding was not provided in 39 trials.
Authors' conclusions: Due to the very low quality evidence, we are very uncertain about the effectiveness of pharmacological treatments for people with NAFLD including those with steatohepatitis. Further well-designed randomised clinical trials with sufficiently large sample sizes are necessary.
Conflict of interest statement
This review is independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR Cochrane Programme Grants, 13/89/03 ‐ Evidence‐based diagnosis and management of upper digestive, hepato‐biliary, and pancreatic disorders). The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the National Health Service (NHS), the NIHR, or the Department of Health.
Kurinchi Gurusamy and Brian Davidson have no financial disclosures. Emmanuel Tsochatzis has participated in advisory boards for Astra Zeneca and ViiV Helthcare. Astellas funded Douglas Thorburn for his attendance at the International Liver Transplantation Society meeting in 2014. Douglas Thorburn has also received GBP 25,000 from Boston Scientific to fund a clinical research fellow in 2013. There are no other financial disclosures to report.
Figures
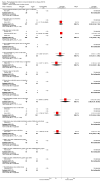
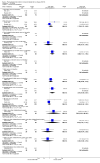
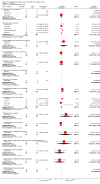


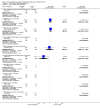
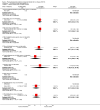
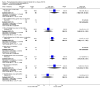
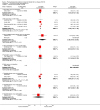
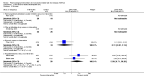






Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Aithal 2008 {published data only}
-
- Aithal GP, Thomas JA, Kaye PV, Lawson A, Ryder SD, Spendlove I, et al. Randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of pioglitazone in nondiabetic subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2008;135(4):1176‐84. - PubMed
Alam 2016 {published data only}
-
- Alam S, Kabir J, Das U, Hasan N, Alam AK. Effect of telmisartan on histological activity and fibrosis of non alcoholic steatohepatitis patient a one year randomized control trial. Hepatology International 2015;9(Suppl 1):S116.
Aller 2015 {published data only}
-
- Aller R, Izaola O, Gomez S, Tafur C, Gonzalez G, Berroa E, et al. Effect of silymarin plus vitamin E in patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. A randomized clinical pilot study. European Review for Medical & Pharmacological Sciences 2015;19(16):3118‐24. - PubMed
Armstrong 2016 {published data only}
-
- Armstrong MJ, Gaunt P, Aithal GP, Barton D, Hull D, Parker R, et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis (lean): A multicentre, double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 2016;387(10019):679‐90. - PubMed
Askarimoghadam 2013 {published data only}
-
- Askarimoghadam F, Arjmandpour A, Adibi P. Effects of metformin plus vitamin E versus metformin alone in treatment of NAFLD: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2013;28:633.
Athyros 2006 {published data only}
-
- Athyros VG, Mikhailidis DP, Didangelos TP, Giouleme OI, Liberopoulos EN, Karagiannis A, et al. Effect of multifactorial treatment on non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in metabolic syndrome: a randomised study. Current Medical Research & Opinion 2006;22(5):873‐83. - PubMed
-
- Athyros VG, Mikhailidis DP, Papageorgiou AA, Didangelos TP, Peletidou A, Kleta D, et al. Targeting vascular risk in patients with metabolic syndrome but without diabetes. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental 2005;54(8):1065‐74. - PubMed
Baranova 2015 {published data only}
-
- Baranova EI, Berezina AV, Melioranskaya EI, Polyakova EA. Safety and efficacy of amlodipine, lisinopril and rosuvastatin therapy in patients with metabolic syndrome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Kardiologiya 2015;55(10):68‐75. - PubMed
Basu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Basu P, Mittimani K, Siriki R, Rahaman M, Atluri S, Farhat S, et al. Curcumin, anti‐oxidant, and pioglitazone therapy with inclusion of vitamin E in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease‐a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial (captive). Hepatology International 2013;7:S73‐4.
-
- Basu P, Shah N, Siriki R, Rahaman M, Farhat S. Curcumin, antioxidant, and pioglitazone therapy with inclusion of vitamin E in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, open‐label, placebo‐controlled clinical prospective trial (captive). American Journal of Gastroenterology 2013;108:S149‐50.
-
- Basu P, Shah NJ, Farhat S, Siriki R, Mittimanj K, Atluri S, et al. Curcumin, anti‐oxidant, and pioglitazone therapy with inclusion of vitamin E in non alcoholic fatty liver disease‐a randomized open label placebo controlled clinical prospective trial (captive). Gut 2013;62:A23‐4.
-
- Basu P, Shah NJ, Siriki R, Mittimani K, Atluri S, Rahaman A, et al. Curcumin, anti‐oxidant, and pioglitazone therapy with inclusion of vitamin E in non alcoholic fatty liver disease‐a randomized open label placebo controlled clinical prospective trial (captive). Gastroenterology 2013;144(5):S1011‐2.
Basu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Basu P, Shah NJ, Farhat S. Effect of vitamin E and alfa lipoic acid (ala) in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomise placebo control open label prospective clinical trial: VAIN trial. Gut 2012;61:A204‐5.
-
- Basu P, Shah NJ, Krishnaswamy N, Farhat S, Nair T. Effect of vitamin E and alfa lipoic acid in non alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2012;27:208.
-
- Basu PP, Krishnaswamy N, Nair T, Shah NJ, Farhat S. Effect of vitamin E and alfa lipoic acid (ala) in non alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized placebo control open label prospective clinical trial ‐ VAIN trial. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2011;106:S136‐7.
-
- Basu PP, Krishnaswamy N, Nair TJ, Shah NJ, Farhat S. Effect of vitamin E and alfa lipoic acid (ala) in non alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized placebo control open label prospective clinical trial ‐ VAIN trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2011;54:1145A‐6A.
-
- Basu PP, Shah JN, Krishnaswamy NV, Pacana T, Khemani J, Farhat S, et al. Effect of vitamin E and alpha lipoic acid (ala) in non alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized placebo‐controlled open‐label prospective clinical trial ‐ VAIN trial. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2012;47:S63‐5.
Belfort 2006 {published data only}
-
- Balas B, Belfort R, Harrison SA, Darland C, Finch J, Schenker S, et al. Pioglitazone treatment increases whole body fat but not total body water in patients with non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis. Journal of Hepatology 2007;47(4):565‐70. - PubMed
-
- Belfort R, Harrison SA, Brown K, Darland C, Finch J, Hardies J, et al. A placebo‐controlled trial of pioglitazone in subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;355(22):2297‐307. - PubMed
Bonfrate 2015 {published data only}
-
- Bonfrate L, Grattagliano I, Portincasa P. The efficacy of eurosil 85‐vit. E complex on metabolic profile in adults with non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). A double‐blind randomized placebo‐controlled clinical study. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2015;45:15.
Bugianesi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bugianesi E, Gentilcore E, Manini R, Natale S, Vanni E, Villanova N, et al. A randomized controlled trial of metformin versus vitamin E or prescriptive diet in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2005;100(5):1082‐90. - PubMed
Chan 2015 {published data only}
-
- Chan WK, Nik Mustapha NR, Mahadeva S. Silymarin for the treatment of non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis: Interim analysis of a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Hepatology 2015;62:S269.
Copaci 2009 {published data only}
-
- Copaci I, Mindrut E, Micu L, Hortopan M, Voiculescu M. Can disease progression in non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis be stopped?. Journal of Hepatology 2009;50:S358.
Cui 2006 {published data only}
-
- Cui KQ, Zhao XW, Zhang Y, Kang XH, Meng J, Chen XL. Efficacy of rosiglitazone in treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its relations with adiponectin. World Chinese Journal of Digestology 2006;14(13):1326‐9.
Cusi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cusi K, Orsak B, Lomonaco R, Bril F, Ortiz‐Lopez C, Hecht J, et al. Extended treatment with pioglitazone improves liver histology in patients with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes mellitus and NASH. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2013;58(Suppl S1):248A.
-
- Cusi K, Orsak B, Lomonaco R, Finch J, Ortiz‐Lopez C, Bril F, et al. Safety and efficacy of long‐term pioglitazone treatment for patients with prediabetes or t2dm and NASH. Diabetes 2013;62:A309.
Dufour 2006 {published data only}
-
- Balmer ML, Siegrist K, Zimmermann A, Dufour JF. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid in combination with vitamin E on adipokines and apoptosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver International 2009;29(8):1184‐8. - PubMed
-
- Dufour J, Oneta CM, Gonvers J, Bihl F, Cerny A, Cereda J, et al. Randomized placebo‐controlled trial of ursodeoxycholic acid with vitamin E in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2006;4(12):1537‐43. - PubMed
Ersoz 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ersoz G, Gunsar F, Karasu Z, Akay S, Batur Y, Akarca US. Management of fatty liver disease with vitamin E and C compared to ursodeoxycholic acid treatment. Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology 2005;16(3):124‐8. - PubMed
Fogari 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fogari R, Maffioli P, Mugellini A, Zoppi A, Lazzari P, Derosa G. Effects of losartan and amlodipine alone or combined with simvastatin in hypertensive patients with nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2012;24(2):164‐71. - PubMed
-
- Fogari R, Mugellini A, Zoppi A, Lazzari P, Maffioli P, Derosa G. Losartan alone or combined with simvastatin improved visceral adipose tissue and inflammation in hypertensive normocholesterolemic patients with non‐alcoholic hepatic steatosis. Journal of Hepatology 2011;54(Suppl 1):S9‐s10.
Foster 2011 {published data only}
-
- Foster T, Budoff MJ, Saab S, Ahmadi N, Gordon C, Guerci AD. Atorvastatin and antioxidants for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the St Francis heart study randomized clinical trial. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2011;106(1):71‐7. - PubMed
Garinis 2010 {published data only}
-
- Garinis GA, Fruci B, Mazza A, Siena M, Abenavoli S, Gulletta E, et al. Metformin versus dietary treatment in nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis: a randomized study. International Journal of Obesity 2010;34(8):1255‐64. - PubMed
Gastaldelli 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gastaldelli A, Balas B, Belfort R, Harrison S, Finch J, Ciociaro D. Metabolic and anti‐inflammatory beneficial effects of pioglitazone (pio) treatment in patients with non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and their associations with histological improvement. Journal of Hepatology 2009;50(Suppl 1):S24.
Gianturco 2013 {published data only}
-
- Gianturco V, Troisi G, Bellomo A, Bernardini S, D'Ottavio E, Formosa V, et al. Impact of combined therapy with alpha‐lipoic and ursodeoxycolic acid on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: double‐blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy and safety. Hepatology International 2013;7(2):570‐6. - PubMed
Gomez 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gomez EV, Miranda AR, Oramas BG, Soler EA, Navarro RL, Bertot LC, et al. Clinical trial: a nutritional supplement viusid, in combination with diet and exercise, in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2009;30(10):999‐1009. - PubMed
Hajaghamohammadi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hajaghamohammadi AA, Ziaee A, Rafiei R. The efficacy of silymarin in decreasing transaminase activities in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Hepatitis Monthly 2008;8(3):191‐5.
Hajiaghamohammadi 2012 {published data only}
Harrison 2003 {published data only}
-
- Harrison SA, Torgerson S, Hayashi P, Ward J, Schenker S. Vitamin E and vitamin C treatment improves fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2003;98(11):2485‐90. - PubMed
Harrison 2009 {published data only}
-
- Harrison SA, Fecht W, Brunt EM, Neuschwander‐Tetri BA. Orlistat for overweight subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, prospective trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2009;49(1):80‐6. - PubMed
Hashemi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hashemi SJ, Hajiani E, Sardabi EH. A placebo‐controlled trial of silymarin in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatitis Monthly 2009;9(4):265‐70.
Haukeland 2009 {published data only}
-
- Haukeland JW, Konopski Z, Eggesbø HB, Volkmann HL, Raschpichler G, Bjøro K, et al. Metformin in patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, controlled trial. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2009;44(7):853‐60. - PubMed
-
- Haukeland JW, Konopski Z, Loberg EM, Haaland TK, Volkmann HL, Raschpichler G, et al. A randomized, placebo controlled trial with metformin in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2008;48(4):334A.
Jin 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jin H, Zhou Y, Ming K. Efficacy of pioglitazone in treatment of 60 patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Pharmaceutical Care and Research 2010;10(3):221‐3.
Kakazu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kakazu E, Kondo Y, Ninomiya M, Kimura O, Nagasaki F, Ueno Y, et al. The influence of pioglitazone on the plasma amino acid profile in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Hepatology International 2013;7(2):577‐85. - PubMed
Kedarisetty 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kedarisetty CK, Bhardwaj A, Bhadoria AS, Bihari C, Rastogi A, Kanal U, et al. A randomized controlled trial to study the efficacy of combination of pentoxiphylline and vitamin E versus vitamin E in patients with non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis. Journal of Hepatology 2014;60(1 Suppl):S344.
Klyarytskaya 2015 {published data only}
-
- Klyarytskaya IL, Stilidi EI, Maksymova EV. Comparison of different treatment regimens in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eksperimental'Naia i Klinicheskaia Gastroenterologiia 2015;7:12‐7. - PubMed
Kugelmas 2003 {published data only}
-
- Kugelmas M, Hill DB, Vivian B, Marsano L, McClain CJ. Cytokines and NASH: A pilot study of the effects of lifestyle modification and vitamin E. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2003;38(2):413‐9. - PubMed
Leuschner 2010 {published data only}
-
- Leuschner UFH, Lindenthal B, Herrmann G, Arnold JC, Rossle M, Cordes HJ, et al. High‐dose ursodeoxycholic acid therapy for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2010;52(2):472‐9. - PubMed
Lewis 2006 {published data only}
-
- Lewis JH, Zweig SF, Belder R. Is the lipid reduction seen with high‐dose pravastatin (prava) associated with a fall in alt values in hypercholesterolemic pts with NAFLD? Results from a prospective, randomized double‐blind, placebo (pbo)‐controlled trial. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2006;101(9):S158‐9.
Lindor 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lindor KD, Kowdley KV, Heathcote EJ, Harrison ME, Jorgensen R, Angulo P, et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid for treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: results of a randomized trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2004;39(3):770‐8. - PubMed
Loomba 2015 {published data only}
-
- Loomba R, Sirlin CB, Ang B, Bettencourt R, Jain R, Salotti J, et al. Ezetimibe for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Assessment by novel magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance elastography in a randomized trial (Mozart trial). Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2015;61(4):1239‐50. - PMC - PubMed
Magosso 2013 {published data only}
-
- Magosso E, Ansari MA, Gopalan Y, Shuaib IL, Khan N, Yuen KH, et al. Tocotrienols and nonalcoholic fatty liver: a clinical experience. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2010;52:642A.
Mendez‐Sanchez 2004 {published data only}
-
- Mendez‐Sanchez N, Gonzalez V, Chavez‐Tapia N, Ramos MH, Uribe M. Weight reduction and ursodeoxycholic acid in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Annals of Hepatology 2004;3(3):108‐12. - PubMed
Merat 2003 {published data only}
-
- Merat S, Malekzadeh R, Sohrabi MR, Sotoudeh M, Rakhshani N, Sohrabpour AA, et al. Probucol in the treatment of non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis: a double‐blind randomized controlled study. Journal of Hepatology 2003;38(4):414‐8. - PubMed
Morita 2005 {published data only}
-
- Morita Y, Ueno T, Sasaki N, Tateishi Y, Nagata E, Kage M, et al. Nateglinide is useful for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients with type 2 diabetes. Hepato‐Gastroenterology 2005;52(65):1338‐43. - PubMed
Mudaliar 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mudaliar S, Henry RR, Sanyal AJ, Morrow L, Marschall HU, Kipnes M, et al. Efficacy and safety of the farnesoid x receptor agonist obeticholic acid in patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2013;145(3):574‐82.e1. - PubMed
Nar 2009 {published data only}
-
- Nar A, Gedik O. The effect of metformin on leptin in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Acta Diabetologica 2009;46(2):113‐8. - PubMed
Nelson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Nelson A, Torres DM, Morgan AE, Fincke C, Harrison SA. A pilot study using simvastatin in the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 2009;43(10):990‐4. - PubMed
Neuschwander‐Tetri 2015 {published data only}
-
- Chalasani NP, Loomba R, Terrault N, McCullough AJ, Abdelmalek MF, Kowdley KV, et al. Longitudinal changes in fib‐4 and improvement in fibrosis stage with obeticholic acid: a secondary analysis of flint trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2015;62:332A‐3A.
-
- Hameed B, Terrault N, Gill R, Loomba R, Chalasani N, Hoofnagle JH, et al. Separate and combined effects of obeticholic acid and weight loss in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Journal of Hepatology 2015;62:S271.
-
- Hameed B, Terrault N, Gill RM, Loomba R, Chalasani NP, Hoofnagle JH, et al. Clinical and metabolic effects associated with weight loss and obeticholic acid in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2015;62:331A.
-
- Kowdley KV, Abdelmalek MF, McCullough A, Loomba R, Hameed B, Chalasani NP, et al. Evaluation of effects of concomitant medications for NASH and associated comorbidities on histological improvements with obeticholic acid. Gastroenterology 2016;150(4 Supple 1):S1144.
-
- Kowdley KV, Abdelmalek MF, McCullough AJ, Loomba R, Hameed B, Chalasani NP, et al. Evaluation of effects of concomitant medications for non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis and associated comorbidities on histological improvements with obeticholic acid. Journal of Hepatology 2016;1:S487‐8.
Omer 2010 {published data only}
-
- Omer Z, Cetinkalp S, Akyildiz M, Yilmaz F, Batur Y, Yilmaz C, et al. Efficacy of insulin‐sensitizing agents in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2010;22(1):18‐23. - PubMed
Parikh 2016 {published data only}
Polyzos 2011 {published data only}
-
- Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Zafeiriadou E, Patsiaoura K, Katsiki E, Deretzi G, et al. Effect of spironolactone and vitamin E on serum metabolic parameters and insulin resistance in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of the Renin‐Angiotensin‐Aldosterone System 2011;12(4):498‐503. - PubMed
Ratziu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lemoine M, Serfaty L, Cervera P, Capeau J, Ratziu V. Hepatic molecular effects of rosiglitazone in human non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis suggest long‐term pro‐inflammatory damage. Hepatology Research 2014;44(12):1241‐7. - PubMed
-
- Ratziu V, Giral P, Jacqueminet S, Charlotte F, Hartemann‐Heurtier A, Serfaty L, et al. Rosiglitazone for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: one‐year results of the randomized placebo‐controlled fatty liver improvement with rosiglitazone therapy (FLIRT) trial. Gastroenterology 2008;135(1):100‐10. - PubMed
Ratziu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ratziu V, Ledinghen V, Oberti F, Mathurin P, Wartelle‐Bladou C, Renou C, et al. A multicentric, double‐blind, randomised‐controlled trial (RCT) of high dose ursodeoxycholic acid in patients with non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Journal of Hepatology 2009;50:S21.
-
- Ratziu V, Ledinghen V, Oberti F, Mathurin P, Wartelle‐Bladou C, Renou C, et al. A randomized controlled trial of high‐dose ursodesoxycholic acid for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Journal of Hepatology 2011;54(5):1011‐9. - PubMed
Ratziu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ratziu V, Bedossa P, Francque SM, Larrey D, Aithal GP, Serfaty L, et al. Lack of efficacy of an inhibitor of pde4 in phase 1 and 2 trials of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2014;12(10):1724‐U202. - PubMed
Ratziu 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ratziu V, Harrison SA, Francque S, Bedossa P, Lehert P, Serfaty L, et al. Elafibranor, an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor‐alpha and ‐delta, induces resolution of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis without fibrosis worsening. Gastroenterology 2016;150(5):1147‐59. - PubMed
Razavizade 2013 {published data only}
-
- Razavizade M, Jamali R, Arj A, Matini SM, Moraveji A, Taherkhani E. The effect of pioglitazone and metformin on liver function tests, insulin resistance, and liver fat content in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized double blinded clinical trial. Hepatitis Monthly 2013;13(5):e9270. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Razavizadeh M, Arj A. Comparison of the therapeutic effects of pioglitazone and metformin in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2012;27:247.
Razavizadeh 2012 {published data only}
-
- Razavizadeh M, Arj A. Comparison of the therapeutic effects of vitamin E and silimarin in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2012;27:270.
Safadi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Safadi R, Konikoff FM, Mahamid M, Zelber‐Sagi S, Halpern M, Gilat T, et al. The fatty acid‐bile acid conjugate aramchol reduces liver fat content in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2014;12(12):2085‐91. - PubMed
Santos 2003 {published data only}
-
- Santos VN, Lanzoni VP, Szejnfeld J, Shigueoka D, Parise ER. A randomized double‐blind study of the short‐time treatment of obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with ursodeoxycholic acid. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research 2003;36(6):723‐9. - PubMed
Sanyal 2004 {published data only}
-
- Sanyal AJ, Mofrad PS, Contos MJ, Sargeant C, Luketic VA, Sterling RK, et al. A pilot study of vitamin E versus vitamin E and pioglitazone for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2004;2(12):1107‐15. - PubMed
Sanyal 2010 {published data only}
-
- Corey K, Vuppalanchi R, Wilson L, Cummings O, Chalasani NP. Nash resolution is associated with improvements in HDL and triglycerides but not in LDL or non‐HDL‐C. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2014;60:224A‐5A.
Sharma 2012 {published data only}
-
- Sharma BC, Kumar A, Garg V, Reddy RS, Sakhuja P, Sarin SK. A randomized controlled trial comparing efficacy of pentoxifylline and pioglitazone on metabolic factors and liver histology in patients with non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hepatology 2012;2(4):333‐7. - PMC - PubMed
Shields 2009 {published data only}
-
- Shields WW, Thompson KE, Grice GA, Harrison SA, Coyle WJ. The effect of metformin and standard therapy versus standard therapy alone in nondiabetic patients with insulin resistance and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A pilot trial. Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology 2009;2(3):157‐63. - PMC - PubMed
Shiffman 2015 {published data only}
-
- Shiffman M, Freilich B, Vuppalanchi R, Watt K, Burgess G, Morris M, et al. A placebo‐controlled, multicenter, double‐blind, randomised trial of emricasan in subjects with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and raised transaminases. Journal of Hepatology 2015;62:S282.
Siddique 2015 {published data only}
-
- Siddique KU, Reddy H, Rana H, Singhal S, Parihar A, Pandey A. A comparative study of effect of insulin sensitizers and statins in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Diabetes 2015;64:A661.
Sofer 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sofer E, Boaz M, Matas Z, Mashavi M, Shargorodsky M. Treatment with insulin sensitizer metformin improves arterial properties, metabolic parameters, and liver function in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental 2011;60(9):1278‐84. - PubMed
-
- Sofer E, Shargorodsky M. Effect of metformin treatment on circulating osteoprotegerin in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology International 2016;10(1):169‐74. - PubMed
-
- Soifer E, Gavish D, Shargorodsky M. Does metformin treatment influence bone formation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?. Hormone & Metabolic Research 2015;47(8):556‐9. - PubMed
Solhi 2014 {published data only}
Song 2014 {published data only}
-
- Song XX, Jiang T, Kang K, Wen Z. Efficacy of sitagliptin combined with metformin in the initial treatment of type 2 diabetes with non‐alcoholic fatty liver. Chinese Journal of New Drugs 2014;23(2):215‐8.
Stefan 2014 {published data only}
-
- Stefan N, Ramsauer M, Jordan P, Nowotny B, Kantartzis K, Machann J, et al. Inhibition of 11 beta‐hsd1 with ro5093151 for non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2014;2(5):406‐16. - PubMed
Stilidi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Stilidi EI, Klyaritskay IL. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid or ursodeoxycholic acid combined with losartan for treatment of non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis. Journal of Hepatology 2014;60(1 Suppl):S334.
Sunny 2015 {published data only}
-
- Sunny N, Bril F, Kalavalapalli S, Sanchez PP, Maximos M, Biernacki D, et al. Pioglitazone therapy improves insulin suppression of branched chain amino acids in patients with prediabetes or T2DM and NAFLD. Diabetes 2015;64:A341.
Taghvaei 2013 {published data only}
-
- Taghvaei T, Bahar A, Hosseini V, Maleki I, Kasrai M. Efficacy of silymarin on treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences 2013;23(98):164‐71.
Torres 2011 {published data only}
-
- Torres D, Jones FJ, Shaw J, Williams C, Ward JA, Harrison SA. Open‐label prospective randomized 48 week clinical trial: rosiglitazone versus rosiglitazone and metformin (avandamet) versus rosiglitazone and losartan in the treatment of non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Journal of Hepatology 2011;54:S7‐8. - PubMed
-
- Torres DM, Jones FJ, Shaw JC, Williams CD, Ward JA, Harrison SA. Rosiglitazone versus rosiglitazone and metformin versus rosiglitazone and losartan in the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in humans: a 12‐month randomized, prospective, open‐ label trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2011;54(5):1631‐9. - PubMed
Uygun 2004 {published data only}
-
- Uygun A, Kadayifci A, Isik AT, Ozgurtas T, Deveci S, Tuzun A, et al. Metformin in the treatment of patients with non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2004;19(5):537‐44. - PubMed
Van Wagner 2011 {published data only}
-
- Wagner LB, Koppe SWP, Brunt EM, Gottstein J, Gardikiotes K, Green RM, et al. Pentoxifylline for the treatment of non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized controlled trial. Annals of Hepatology 2011;10(3):277‐86. - PubMed
Wang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wang X, Zhao B, Cheng Y, Bu L, Qu S. Sitagliptin decreases intrahepatic lipid accumulation in diabetic patients with NAFLD. Diabetes 2015;64:A620‐1.
Yaginuma 2009 {published data only}
-
- Yaginuma R, Ikejima K, Kon K, Okumura K, Yamashina S, Suzuki S, et al. Efficacy of low‐dose pioglitazone for the treatment of NAFLD patients in japan. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2009;50:793A‐4A.
Yan 2015 {published data only}
-
- Yan H, Xia M, Chang X, Bian H, Lin H, Zhang L, et al. Berberine vs. pioglitazone for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its associated impaired glucose metabolism. Diabetes 2014;63:A513‐4.
References to studies excluded from this review
Abenavoli 2013 {published data only}
-
- Abenavoli L, Nazionale I, Greco M, Larussa T, Suraci E, Imeneo M, et al. Metabolic effects of diet vs diet and silybin combined with phosphatidylcholine and vitamin E in overweight patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. Digestive and Liver Disease 2013;45:S165‐6.
Abenavoli 2015 {published data only}
-
- Abenavoli L, Greco M, Nazionale I, Peta V, Milic N, Accattato F, et al. Effects of Mediterranean diet supplemented with silybin‐vitamin E‐phospholipid complex in overweight patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2015;9(4):519‐27. - PubMed
Acquati 2007 {published data only}
-
- Acquati S, Silvani G, Bondi A, Cicognani R, Bondi G, Gagliardi L, et al. Beyond glycated haemoglobin: effectiveness of rosiglitazone in type‐2 diabetes with hypertension and non‐alcoholic fatty liver. A randomized controlled one‐year study. Atherosclerosis Supplements 2007;8(1):191.
Athyros 2011 {published data only}
-
- Athyros VG, Giouleme O, Ganotakis ES, Elisaf M, Tziomalos K, Vassiliadis T, et al. Safety and impact on cardiovascular events of long‐term multifactorial treatment in patients with metabolic syndrome and abnormal liver function tests: a post hoc analysis of the randomised attempt study. Archives of Medical Science 2011;7(5):796‐805. - PMC - PubMed
Carnelutti 2012 {published data only}
-
- Carnelutti A, Donnini D, Nadalutti G, Luca L, Cappello D, Cugini F, et al. Effect of statin therapy vs diet in hypercholesterolemic patients affected by nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Digestive and Liver Disease 2012;44:S25‐6.
Corey 2015a {published data only}
Dajani 2015 {published data only}
-
- Dajani AIM, Abu Hammour AM, Zakaria MA, Al Jaberi MR, Nounou MA, Semrin AIM. Essential phospholipids as a supportive adjunct in the management of patients with NAFLD. Arab Journal of Gastroenterology 2015;16(3‐4):99‐104. - PubMed
Faghihzadeh 2014 {published data only}
-
- Faghihzadeh F, Adibi P, Rafiei R, Hekmatdoost A. Resveratrol supplementation improves inflammatory biomarkers in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrition Research 2014;34(10):837‐43. - PubMed
Fan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Fan XF, Deng YQ, Ye L, Li YD, Chen J, Lu WW, et al. Effect of xuezhikang capsule on serum tumor necrosis factor‐alpha and interleukin‐6 in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hyperlipidemia. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 2010;16(2):119‐23. - PubMed
Fan 2013 {published data only}
-
- Fan H, Pan Q, Xu Y, Yang X. Exenatide improves type 2 diabetes concomitant with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia e Metabologia 2013;57(9):702‐8. - PubMed
Gastaldelli 2015 {published data only}
-
- Gastaldelli A, Tripathy D, Gaggini M, Musi N, DeFronzo RA. Improvement in hepatic metabolism is associated with reduced conversion to diabetes in IGT subjects treated with pioglitazone (act now study). Diabetologia 2015;58(Suppl 1):S164.
Han 2012 {published data only}
-
- Han KH, Rha SW, Kang HJ, Bae JW, Choi BJ, Choi SY, et al. Evaluation of short‐term safety and efficacy of HMG‐CoA reductase inhibitors in hypercholesterolemic patients with elevated serum alanine transaminase concentrations: PITCH study (PITavastatin versus atorvastatin to evaluate the effect on patients with hypercholesterolemia and mild to moderate hepatic damage). Journal of Clinical Lipidology 2012;6(4):340‐51. - PubMed
Han 2014a {published data only}
-
- Han Y, Shi JP, Ma AL, Xu Y, Ding XD, Fan JG. Randomized, vitamin E‐controlled trial of bicyclol plus metformin in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease patients with impaired fasting glucose. Clinical Drug Investigation 2014;34(1):1‐7. - PubMed
Idilman 2008 {published data only}
-
- Idilman R, Mizrak D, Corapcioglu D, Bektas M, Doganay B, Sayki M, et al. Clinical trial: Insulin‐sensitizing agents may reduce consequences of insulin resistance in individuals with non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2008;28(2):200‐8. - PubMed
Jaafari 2012 {published data only}
-
- Jaafari Haidarlo A, Rashidbeygi M, Ehsanbakhsh S. Vitamin E, pioglitazone and diet therapy for patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): evaluation of treatment. Journal of Hepatology 2012;56(Suppl 2):S507.
Kowdley 2015 {published data only}
-
- Kowdley KV, Wilson LA, Natta ML, Pai RK, Sanyal AJ. Efficacy and safety of vitamin E for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Combined analysis of three controlled trials. Journal of Hepatology 2015;62:S268.
Kowdley 2015a {published data only}
-
- Kowdley KV, Wilson LA, Natta ML, Pai RK, Sanyal AJ. Efficacy and safety of vitamin E in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients with and without diabetes: pooled analysis from the PIVENS and FLINT NIDDK NASH CRN trials. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2015;62:264A.
Li 2015 {published data only}
Lo 2016 {published data only}
McCormick 2015 {published data only}
-
- McCormick KG, Scorletti E, Bhatia L, Calder PC, Griffin MJ, Clough GF, et al. Impact of high dose n‐3 polyunsaturated fatty acid treatment on measures of microvascular function and vibration perception in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: Results from the randomised welcome trial. Diabetologia 2015;58(8):1916‐25. - PubMed
Merat 2015 {published data only}
-
- Merat S, Poustchi H, Hemming K, Jafari E, Radmard AR, Nateghi A, et al. Polypill for prevention of cardiovascular disease in an urban Iranian population with special focus on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a pragmatic randomized controlled trial within a cohort (polyiran ‐ liver) ‐ study protocol. Archives of Iranian Medicine 2015;18(8):515‐23. - PubMed
Oh 2016 {published data only}
-
- Oh B, Choi WS, Park SB, Cho B, Yang YJ, Lee ES, et al. Efficacy and safety of ursodeoxycholic acid composite on fatigued patients with elevated liver function and/or fatty liver: a multi‐centre, randomised, double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled trial. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2016;70(4):302‐11. - PMC - PubMed
Scorletti 2014 {published data only}
-
- Scorletti E, Bhatia L, McCormick KG, Clough GF, Nash K, Hodson L, et al. Effects of purified eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: results from the Welcome* study. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2014;60(4):1211‐21. - PubMed
Scorletti 2015 {published data only}
-
- Scorletti E, West AL, Bhatia L, Hoile SP, McCormick KG, Burdge GC, et al. Treating liver fat and serum triglyceride levels in NAFLD, effects of pnpla3 and tm6sf2 genotypes: results from the Welcome trial. Journal of Hepatology 2015;63(6):1476‐83. - PubMed
Shiasi 2014 {published data only}
Sultana 2012 {published data only}
-
- Sultana SS, Amin F, Rahman A, Afsana F. A comparative study with metformin and pioglitazone versus metformin alone in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in newly detected glucose intolerant patients. Diabetologia 2012;55:S500.
Talebi 2015 {published data only}
-
- Talebi Pour B, Jameshorani M, Salmani R, Chiti H. The effect of chlorella vulgaris vs. Artichoke on patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Zanjan University of Medical Sciences and Health Services 2015;23(100):36‐44.
Tan 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tan HH, Low ASC, Lim KH, Wan WK, Goh BB, Wang YT, et al. A randomized, unblinded pilot trial of essential phospholipids in Chinese subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NASH). Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2011;26:162.
Taniai 2009 {published data only}
-
- Taniai M, Hashimoto E, Tobari M, Yatsuji S, Haruta I, Tokushige K, et al. Treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with colestimide. Hepatology Research 2009;39(7):685‐93. - PubMed
Tsuchiya 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tsuchiya M. Alogliptin decreases liver fat content in patients with IGT or type Q2 DM: comparing alogliptin and voglibose. Diabetes 2011;60:A595.
Vos 2016 {published data only}
-
- Vos M, Jin R, Welsh J, Konomi J, Karpen SJ, Soler‐Rodriquez D, et al. Losartan improves hepatic inflammation in children with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2016;150(4):S1036.
Wang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wang Q, Lao J, Zou X, Huang Y. Clinical effect of metformin combined with reduced glutathione in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2013;28:186.
Zelber‐Sagi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Zelber‐Sagi S, Kessler A, Brazowsky E, Webb M, Lurie Y, Santo M, et al. A double‐blind randomized placebo‐controlled trial of orlistat for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clinical Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2006;4(5):639‐44. - PubMed
-
- Zelber‐Sagi S, Kessler A, Brazowsky E, Webb M, Lurie Y, Santo M, et al. Randomized placebo‐controlled trial of orlistat for the treatment of patients with non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2004;40(4 Supl 1):237a. - PubMed
Additional references
Abdelmalek 2007
-
- Abdelmalek MF, Diehl AM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a complication of insulin resistance. Medical Clinics of North America 2007;91(6):1125‐49, ix. - PubMed
Abenavoli 2013a
-
- Abenavoli L, Bellentani S. Milk thistle to treat non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: dream or reality?. Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2013;7(8):677‐9. - PubMed
Adams 2005
-
- Adams LA, Lymp JF, Sauver J, Sanderson SO, Lindor KD, Feldstein A, et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population‐based cohort study. Gastroenterology 2005;129(1):113‐21. - PubMed
Adorini 2012
-
- Adorini L, Pruzanski M, Shapiro D. Farnesoid X receptor targeting to treat nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Drug Discovery Today 2012;17(17‐18):988‐97. - PubMed
Alberti 2009
-
- Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009;120(16):1640‐5. - PubMed
Angulo 2015
Anstee 2012
-
- Anstee QM, Day CP. S‐adenosylmethionine (SAMe) therapy in liver disease: a review of current evidence and clinical utility. Journal of Hepatology 2012;57(5):1097‐109. - PubMed
Ballestri 2016
-
- Ballestri S, Zona S, Targher G, Romagnoli D, Baldelli E, Nascimbeni F, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an almost twofold increased risk of incident type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Evidence from a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2016;31(5):936‐44. - PubMed
Bedogni 2005
-
- Bedogni G, Miglioli L, Masutti F, Tiribelli C, Marchesini G, Bellentani S. Prevalence of and risk factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the Dionysos nutrition and liver study. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2005;42(1):44‐52. - PubMed
Bedogni 2007
-
- Bedogni G, Miglioli L, Masutti F, Castiglione A, Croce LS, Tiribelli C, et al. Incidence and natural course of fatty liver in the general population: the Dionysos study. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2007;46(5):1387‐91. - PubMed
Buzetti 2017
-
- Buzzetti E, Kalafateli M, Thorburn D, Davidson BR, Thiele M, Gluud LL, et al. Pharmacological interventions for alcoholic liver disease (alcohol‐related liver disease): a network meta‐analysis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011646.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Chaimani 2012
-
- Chaimani A, Salanti G. Using network meta‐analysis to evaluate the existence of small‐study effects in a network of interventions. Research Synthesis Methods 2012;3(2):161‐76. - PubMed
Chaimani 2013
Chalasani 2012
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl AM, Brunt EM, Cusi K, et al. The diagnosis and management of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology 2012;55(6):2005‐23. - PubMed
Chan 2013
Dassanayake 2009
-
- Dassanayake AS, Kasturiratne A, Rajindrajith S, Kalubowila U, Chakrawarthi S, Silva AP, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease among adults in an urban Sri Lankan population. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2009;24(7):1284‐8. - PubMed
Del Re 2013
DeMets 1987
-
- DeMets DL. Methods for combining randomized clinical trials: strengths and limitations. Statistics in Medicine 1987;6(3):341‐50. - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177‐88. - PubMed
Dias 2010
-
- Dias S, Welton NJ, Caldwell DM, Ades AE. Checking consistency in mixed treatment comparison meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2010;29(7‐8):932‐44. - PubMed
Dias 2012a
-
- Dias S, Welton NJ, Sutton AJ, Ades AE. NICE DSU Technical Support Document 1: introduction to evidence synthesis for decision making, April 2011 (last updated April 2012). www.nicedsu.org.uk/TSD1%20Introduction.final.08.05.12.pdf (accessed 27 March 2014).
Dias 2012b
-
- Dias S, Sutton AJ, Welton NJ, Ades AE. NICE DSU Technical Support Document 3: heterogeneity: subgroups, meta‐regression, bias and bias‐adjustment, September 2011 (last updated April 2012). www.nicedsu.org.uk/TSD3%20Heterogeneity.final%20report.08.05.12.pdf (accessed 27 March 2014).
Dias 2014a
-
- Dias S, Welton NJ, Sutton AJ, Caldwell DM, Lu G, Ades AE. NICE DSU Technical Support Document 4: inconsistency in networks of evidence based on randomised controlled trials, May 2011 (last updated April 2014). www.nicedsu.org.uk/TSD4%20Inconsistency.final.15April2014.pdf (accessed 8 October 2014). - PubMed
Dias 2014b
-
- Dias S, Welton NJ, Sutton AJ, Ades AE. NICE DSU Technical Support Document 2: a generalised linear modelling framework for pair wise and network meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials, August 2011 (last updated April 2014). www.nicedsu.org.uk/TSD2%20General%20meta%20analysis%20corrected%2015Apri... (accessed 8 October 2014).
Dongiovanni 2015
-
- Dongiovanni P, Petta S, Mannisto V, Mancina RM, Pipitone R, Karja V, et al. Statin use and non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis in at risk individuals. Journal of Hepatology 2015;63(3):705‐12. - PubMed
Egger 1997
EuroQol 2014
-
- EuroQol. About EQ‐5D, 2014. www.euroqol.org/about‐eq‐5d.html (accessed 8 October 2014).
Fleischman 2014
Gluud 2007
-
- Gluud C, Brok J, Gong Y, Koretz RL. Hepatology may have problems with putative surrogate outcome measures. Journal of hepatology 2007;46(4):734‐42. [PUBMED: 17316871] - PubMed
Gluud 2016
-
- Gluud C, Nikolova D, Klingenberg SL. Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group. About The Cochrane Collaboration (Cochrane Review Groups (CRGs)) 2016, Issue 10. Art. No.: LIVER.
Gurung 2013
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction ‐ GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383‐94. - PubMed
Hernaez 2011
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2012
ICH‐GCP 1997
-
- International Conference on Harmonisation Expert Working Group. International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline. Guideline for Good Clinical Practice CFR & ICH Guidelines. Vol. 1, Philadelphia (PA): Barnett International/PAREXEL, 1997.
Jakobsen 2014
Ji 2014
-
- Ji HF, Sun Y, Shen L. Effect of vitamin E supplementation on aminotransferase levels in patients with NAFLD, NASH, and CHC: results from a meta‐analysis. Nutrition 2014;30(9):986‐91. - PubMed
Kjaergard 2001
-
- Kjaergard LL, Villumsen J, Gluud C. Reported methodologic quality and discrepancies between large and small randomized trials in meta‐analyses. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;135(11):982‐9. - PubMed
Koehler 2012
-
- Koehler EM, Schouten JN, Hansen BE, Rooij FJ, Hofman A, Stricker BH, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in the elderly: results from the Rotterdam study. Journal of Hepatology 2012;57(6):1305‐11. - PubMed
Lazo 2013
Li 2011
Li 2013
Li 2014
-
- Li Z, Xue J, Chen P, Chen L, Yan S, Liu L. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mainland of China: a meta‐analysis of published studies. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2014;29(1):42‐51. - PubMed
Lirussi 2007
Lonardo 2015
-
- Lonardo A, Bellentani S, Argo CK, Ballestri S, Byrne CD, Caldwell SH, et al. Epidemiological modifiers of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: Focus on high‐risk groups. Digestive and Liver Disease 2015;47(12):997‐1006. - PubMed
Lu 2006
-
- Lu G, Ades AE. Assessing evidence inconsistency in mixed treatment comparisons. Journal of the American Statistical Association 2006;101(474):447‐59.
Lundh 2017
Macaskill 2001
-
- Macaskill P, Walter SD, Irwig L. A comparison of methods to detect publication bias in meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(4):641‐54. - PubMed
Mahady 2011
-
- Mahady SE, Webster AC, Walker S, Sanyal A, George J. The role of thiazolidinediones in non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis ‐ a systematic review and meta analysis. Journal of Hepatology 2011;55(6):1383‐90. - PubMed
Mills 2012
-
- Mills EJ, Ioannidis JP, Thorlund K, Schünemann HJ, Puhan MA, Guyatt GH. How to use an article reporting a multiple treatment comparison meta‐analysis. JAMA 2012;308(12):1246‐53. - PubMed
Moher 1998
-
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 1998;352(9128):609‐13. - PubMed
NCBI 2014
-
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Fatty liver, 2014. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68005234 (accessed 2 October 2014).
Newell 1992
-
- Newell DJ. Intention‐to‐treat analysis: implications for quantitative and qualitative research. International Journal of Epidemiology 1992;21(5):837‐41. - PubMed
Nishioji 2015
-
- Nishioji K, Sumida Y, Kamaguchi M, Mochizuki N, Kobayashi M, Nishimura T, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in a non‐obese Japanese population, 2011‐2012. Journal of Gastroenterology 2015;50(1):95‐108. - PubMed
Ong 2008
-
- Ong JP, Pitts A, Younossi ZM. Increased overall mortality and liver‐related mortality in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Hepatology 2008;49(4):608‐12. - PubMed
Onnerhag 2014
-
- Onnerhag K, Nilsson PM, Lindgren S. Increased risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer during long‐term follow‐up of patients with biopsy‐proven NAFLD. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2014;49(9):1111‐8. - PubMed
OpenBUGS 3.2.3 [Computer program]
-
- Members of OpenBUGS Project Management Group. OpenBUGS. Version 3.2.3. Members of OpenBUGS Project Management Group, 2014.
Orlando 2007
Park 2006
-
- Park SH, Jeon WK, Kim SH, Kim HJ, Park DI, Cho YK, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease among Korean adults. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2006;21(1 Pt 1):138‐43. - PubMed
Paschos 2012
Puhan 2014
-
- Puhan MA, Schünemann HJ, Murad MH, Li T, Brignardello‐Petersen R, Singh JA, et al. A GRADE Working Group approach for rating the quality of treatment effect estimates from network meta‐analysis. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.) 2014;349:g5630. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Riley 2007
Rinella 2015
-
- Rinella ME. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review. JAMA 2015;313(22):2263‐73. - PubMed
Royle 2003
-
- Royle P, Milne R. Literature searching for randomized controlled trials used in Cochrane reviews: rapid versus exhaustive searches. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 2003;19(4):591‐603. - PubMed
Saffioti 2017a
Saffioti 2017b
Salanti 2011
-
- Salanti G, Ades AE, Ioannidis JP. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple‐treatment meta‐analysis: an overview and tutorial. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(2):163‐71. - PubMed
Salanti 2012
-
- Salanti G. Indirect and mixed‐treatment comparison, network, or multiple‐treatments meta‐analysis: many names, many benefits, many concerns for the next generation evidence synthesis tool. Research Synthesis Methods 2012;3(2):80‐97. - PubMed
Sanyal 2016
Savović 2012a
-
- Savović J, Jones HE, Altman DG, Harris RJ, Jüni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomized controlled trials: combined analysis of meta‐epidemiological studies. Health Technology Assessment 2012;16(35):1‐82. - PubMed
Savović 2012b
-
- Savović J, Jones HE, Altman DG, Harris RJ, Jüni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomized controlled trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2012;157(6):429‐38. - PubMed
Sawangjit 2016
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408‐12. - PubMed
Schulz 2010
Severini 1993
-
- Severini TA. Bayesian interval estimates which are also confidence intervals. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological) 1993;55(2):533‐40.
Shen 2014
-
- Shen H, Shahzad G, Jawairia M, Bostick RM, Mustacchia P. Association between aspirin use and the prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a cross‐sectional study from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2014;40(9):1066‐73. - PubMed
Singh 2015
-
- Singh S, Khera R, Allen AM, Murad MH, Loomba R. Comparative effectiveness of pharmacological interventions for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a systematic review and network meta‐analysis. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2015;62(5):1417‐32. - PubMed
Soderberg 2010
-
- Soderberg C, Stal P, Askling J, Glaumann H, Lindberg G, Marmur J, et al. Decreased survival of subjects with elevated liver function tests during a 28‐year follow‐up. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2010;51(2):595‐602. - PubMed
Stata/SE 14.2 [Computer program]
-
- StataCorp LP. Stata/SE 14.2 for Windows[64‐bit x86‐64]. Version 14. College Station: StataCorp LP, 2017.
Thoma 2012
-
- Thoma C, Day CP, Trenell MI. Lifestyle interventions for the treatment of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults: a systematic review. Journal of Hepatology 2012;56(1):255‐66. - PubMed
Thorlund 2011
-
- Thorlund K, Engstrøm J, Wetterslev J, Brok J, Imberger G, Gluud C. User manual for Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA). ctu.dk/tsa/files/tsa_manual.pdf 2011 (accessed 28 November 2016).
Thorlund 2012
TSA 2011 [Computer program]
-
- Copenhagen Trial Unit, Centre for Clinical Intervention Research, Copenhagen. TSA version 0.9. Copenhagen Trial Unit, Centre for Clinical Intervention Research, Copenhagen, 2011.
Turner 2012
Van Valkenhoef 2012
-
- Valkenhoef G, Lu G, Brock B, Hillege H, Ades AE, Welton NJ. Automating network meta‐analysis. Research Synthesis Methods 2012;3(4):285‐99. - PubMed
Ware 2014
-
- Ware JE. SF‐36 health survey update, 2014. www.sf‐36.org/tools/sf36.shtml (accessed 8 October 2014).
Wetterslev 2008
-
- Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C. Trial sequential analysis may establish when firm evidence is reached in cumulative meta‐analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(1):64‐75. - PubMed
Wetterslev 2017
Wood 2008
Xiang 2013
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

