HR+, HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer and CDK4/6 Inhibitors: Mode of Action, Clinical Activity, and Safety Profiles
- PMID: 28359238
- PMCID: PMC5652078
- DOI: 10.2174/1568009617666170330120452
HR+, HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer and CDK4/6 Inhibitors: Mode of Action, Clinical Activity, and Safety Profiles
Abstract
Background: Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor-based therapies have shown great promise in improving clinical outcomes for patients with hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) advanced breast cancer.
Objectives: 1. Discuss the mode of action of the three CDK4/6 inhibitors in late clinical development: palbociclib (PD-0332991; Pfizer), ribociclib (LEE011; Novartis), and abemaciclib (LY2835219; Lilly). 2. Describe the efficacy and safety data relating to their use in HR+, HER2- advanced breast cancer. 3. Discuss the key side effects associated with CDK4/6 inhibitors along with considerations for adverse event management and patient monitoring.
Method: Relevant information and data were assimilated from manuscripts, congress publications, and online sources.
Results: CDK4/6 inhibitors have demonstrated improved progression-free survival in combination with endocrine therapy compared with endocrine therapy alone. The side-effect profile of each agent is described, along with implications for patient monitoring, and considerations for patient care providers and pharmacists.
Conclusion: Addition of a CDK4/6 inhibitor to endocrine therapy increases efficacy and delays disease progression. Insight into the unique side-effect profiles of this class of agents and effective patient monitoring will facilitate the successful use of CDK4/6 inhibitor-based therapies in the clinic.
Keywords: Abemaciclib; CDK4/6 inhibitor; advanced breast cancer; hormone receptor-positive; palbociclib; ribociclib.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
Figures
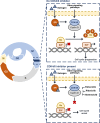
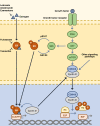
References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer 2012 http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_cancer.aspx
-
- American Cancer Society Cancer facts & figures. 2016 http://www.cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstatistics/index
-
- Platet N., Cathiard A., Gleizes M., Garcia M. Estrogens and their receptors in breast cancer progression: a dual role in cancer proliferation and invasion. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2004;51(1):55–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

