Contemporary Approaches to Modulating the Nitric Oxide-cGMP Pathway in Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 28360348
- PMCID: PMC5391494
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.303776
Contemporary Approaches to Modulating the Nitric Oxide-cGMP Pathway in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
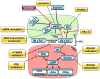
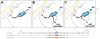
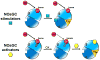
Endothelial cells lining the vessel wall control important aspects of vascular homeostasis. In particular, the production of endothelium-derived nitric oxide and activation of soluble guanylate cyclase promotes endothelial quiescence and governs vasomotor function and proportional remodeling of blood vessels. Here, we discuss novel approaches to improve endothelial nitric oxide generation and preserve its bioavailability. We also discuss therapeutic opportunities aimed at activation of soluble guanylate cyclase for multiple cardiovascular indications.
Keywords: caveolin-1; endothelial cells; heart failure; nitrates; nitric oxide.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Anggard EE. The endothelium--the body’s largest endocrine gland? The Journal of endocrinology. 1990;127:371–375. - PubMed
-
- Molina DK, DiMaio VJ. Normal organ weights in men: Part ii-the brain, lungs, liver, spleen, and kidneys. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2012;33:368–372. - PubMed
-
- His W. Die häute und höhlen des körpers. Basel: Schweighauser; 1865.
-
- Kaiser L, Sparks HV., Jr Endothelial cells: Not just a cellophane wrapper. Archives of Internal Medicine. 1987;147:569–573. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

