Effects of decompression on behavioral, electrophysiologic, and histomorphologic recovery in a chronic sciatic nerve compression model of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- PMID: 28360533
- PMCID: PMC5365322
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S125693
Effects of decompression on behavioral, electrophysiologic, and histomorphologic recovery in a chronic sciatic nerve compression model of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
Abstract
Purpose: To determine susceptibility to decompression surgery in diabetic and nondiabetic peripheral neuropathy using a chronic compression neuropathy model.
Materials and methods: Twenty-four streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats were randomly divided into three groups: group I, chronic compression of the left sciatic nerve for 4 weeks with decompression; group II, similar without decompression; and group III, sham exposing the sciatic nerve only. The other 24 nondiabetic rats were assigned to groups IV-VI, which received compression-decompression, compression, and the sham operation, respectively. Mixed-nerve-elicited somatosensory evoked potentials (M-SSEPs) and compound muscle action potentials (CMAPs) were measured to verify the compression neuropathy in the posttreatment follow-up. Behavioral observations in thermal hyperalgesia tests were quantified before electrophysiologic examinations. Treated and contralateral nerves were harvested for histomorphologic analysis.
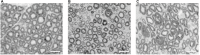
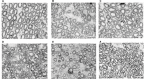
Results: Chronic compression of sciatic nerve induced significant reduction of amplitude and increment of latency of M-SSEP and CMAP in both diabetic and nondiabetic rats. Diabetic group changes were more susceptible. Decompression surgery significantly improved both sensory and motor conduction, thermal hyperalgesia, and the mean myelin diameter of the rat sciatic nerve in both diabetic and nondiabetic groups. Near full recovery of motor and sensory function occurred in the nondiabetic rats, but not in the diabetic rats 8 weeks postdecompression.
Conclusion: Behavioral, electrophysiologic, and histomorphologic findings indicate that decompression surgery is effective in both diabetic and nondiabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Keywords: compression; decompression; diabetes; rat; sciatic nerve; streptozotocin.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Dyck PJ, Kratz KM, Karnes JL, et al. The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology. 1993;43(4):817–824. - PubMed
-
- Young MJ, Boulton AJ, MacLeod AF, Williams DR, Sonksen PH. A multicentre study of the prevalence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in the United Kingdom hospital clinic population. Diabetologia. 1993;36(2):150–154. - PubMed
-
- Gordois A, Scuffham P, Shearer A, Oglesby A, Tobian JA. The health care costs of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in the US. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(6):1790–1795. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

