Students' perceptions of lecturing approaches: traditional versus interactive teaching
- PMID: 28360541
- PMCID: PMC5364003
- DOI: 10.2147/AMEP.S131851
Students' perceptions of lecturing approaches: traditional versus interactive teaching
Abstract
Background: There is an increasing trend toward transcending from traditional teaching to student-centered methodologies that actively engage students. We aimed to analyze students' perceptions of effective interactive teaching using PollEverywhere Audience Response System (ARS) as a worthwhile teaching methodology. It can be of great help in maintaining students' attention and in facilitating the lecturer to pick up students' misunderstandings and correct them.
Materials and methods: This system was introduced to the undergraduate dental curriculum to increase student's motivation and attention, giving immediate feedback on student understanding during an anatomy module. Computer science (CS) students who were more familiar with the use of this technology were also involved in the study for comparison and validation of the findings. The lecturer strategically inserted questions using PollEverywhere ARS. Students' perception of the effective interactive teaching using this technology was evaluated statistically using a questionnaire and focus groups.
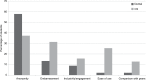
Results: It promoted interactivity, focused attention, and provided feedback on comprehension. A total of 95% reported that it increased their participation and found that it clarified their thinking and helped to focus on key points. Another 81.7% mentioned that it increased their motivation to learn. Students regarded it as a useful method for giving real-time feedback, which stimulated their performance and participation. Data from CS students echoed the findings from the dental students. Reports from focus groups demonstrated that this strategy was helpful in focusing students' attention and in clarifying information.
Discussion: PollEverywhere encouraged all students to participate during the learning process. This has proven to be an effective tool for improving students' understanding and critical thinking.
Conclusion: Students regarded PollEverywhere as an effective teaching innovation that encouraged deeper ongoing retention of information. It was found to be an effective teaching aid in monitoring students' progress and identifying deficiencies. This is of benefit in a module where interactivity is considered important.
Keywords: anatomy; audience response; formative feedback; interactive learning; technology.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Comment in
-
Using mobile audience response systems to enhance medical education: a medical student perspective.Adv Med Educ Pract. 2017 May 5;8:325-327. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S138025. eCollection 2017. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2017. PMID: 28503079 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hutchings B. Principles of Enquiry-Based Learning. Centre for Excellence in Enquiry-Based Learning, University of Manchester; 2006. Available from: http://www.ceebl.manchester.ac.uk/resources/papers/ceeblgr002.pdf.
-
- Walsh S. Exploring Classroom Discourse Language in Action. Oxon: Routledge; 2011.
-
- Hall JK, Verplaetse LS. Second and Foreign Language Learning through Classroom Interaction. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum; 2000.
-
- Gulpinar MA, Yegen BC. Interactive lecturing for meaningful learning in large groups. Med Teach. 2005;27(7):590–594. - PubMed
-
- Berk RA. Survey of twelve strategies to measure teaching effectiveness. Int J Teach Learn Higher Educ. 2005;17:48–62.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

