Association Between Age at Onset of Schizophrenia and Age at Menarche
- PMID: 28360628
- PMCID: PMC5353125
- DOI: 10.4274/npa.y6675
Association Between Age at Onset of Schizophrenia and Age at Menarche
Abstract
Introduction: Increasing evidence from clinical practice, as well as from epidemiological and basic research shows that there are gender differences in clinical features of schizophrenia, and this may be related to estrogens. There may be a relationship between earlier puberty and later onset of the disease, because of the protective effects of estrogens in women with schizophrenia. In this study, our aim was to analyze the correlation between age of menarche and age of onset of schizophrenia and to investigate the protective effects of estrogens in schizophrenia.
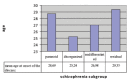
Method: In this study, we included 289 patients who were diagnosed with schizophrenia. Those with mental deficiency or organic brain disorders were excluded from the study. All subjects were given a socio-demographic form to determine their personal information, age at menarche, age at first odd behavior, age at onset of the disease and first hospitalization. Data on factors which may affect the association between age at onset of schizophrenia and age at menarche such as family history, head or birth trauma etc. were recorded on the information form.
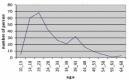
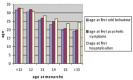
Results: We found out that age at menarche was negatively associated with age at first odd behavior and age at first psychotic symptoms.
Conclusion: Our study verifies the protective effects of estrogens and shows that the earlier puberty may be the cause of later onset of schizophrenia. A gender-sensitive approach in psychiatry improves our understanding of mental illness and our therapeutic strategies.
Giriş: Epidemiyolojik ve laboratuara dayalı araştırmalar kadar klinik kanıtlar da östrojenin kadınların ruhsal durumu üzerinde anlamlı etkisi olduğunu göstermektedir. Bu konu ile ilgili yapılan araştırmalarda şizofrenide belirli özellikler açısından cinsiyete dair farklılıklar olduğu bilinmekte; bunda östrojenin kadın şizofreni hastalarında koruyucu rolünün etkisi olduğu hipotezi öne sürülmektedir. Bu çalışmada, bizim amacımız kadın şizofreni hastalarında şizofreni başlangıç yaşı ile menarş yaşı arasındaki korelasyonu araştırarak, östrojenin şizofrenide koruyucu etkisini sorgulamaktır.
Yöntem: SCID görüşmesi sonucunda şizofreni tanısı onaylanan 289 hasta çalışmaya dahil edildi. Zeka geriliği ya da bilinen organik beyin hastalığı (epilepsi, inme vb.) bulunan hastalar çalışmaya alınmadı. Verilen sosyodemografik form ile hastaların kişisel bilgileri, ilk tuhaf davranış yaşı, şizofreni başlangıç yaşı, ilk hastaneye yatış yaşı ve ilk adet yaşı hasta ve bir yakını ile görüşülerek belirlendi. Şizofreni başlangıç yaşı ile puberte başlangıç yaşı arasındaki ilişkiyi etkileyebilecek olan veriler (aile öyküsü, kafa veya doğum travması gibi) sosyodemografik forma kaydedildi.
Bulgular: Yaptığımız çalışmada menarş yaşı ile ilk tuhaf davranış ve ilk hastalık başlangıç yaşı arasında anlamlı negatif korelasyon olduğu sonucu ortaya çıktı.
Sonuç: Çalışmamız östrojenin koruyucu etkisiyle ilgili verileri desteklemekte; pubertenin erken başlamasının yani erken östrojen salınımının, şizofreni başlangıcının gecikmesine neden olabileceğini göstermektedir. Psikiyatride cinsiyet odaklı bir yaklaşım hastalıkları ve tedavi yaklaşımlarına olan bakış açımızı geliştirecektir.
Keywords: Schizophrenia; age at onset of schizophrenia; gender; menarche age.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors reported no conflict of interest related to this article. Çıkar çatışması: Yazarlar bu makale ile ilgili olarak herhangi bir çıkar çatışması bildirmemişlerdir.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Earlier puberty as a predictor of later onset of schizophrenia in women.Am J Psychiatry. 1999 Jul;156(7):1059-64. doi: 10.1176/ajp.156.7.1059. Am J Psychiatry. 1999. PMID: 10401452
-
Relationship between sex differences in onset of schizophrenia and puberty.J Psychiatr Res. 2000 Jul-Oct;34(4-5):349-53. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3956(00)00030-3. J Psychiatr Res. 2000. PMID: 11104849
-
Age of menarche and schizophrenia onset in women.Schizophr Res. 2004 Aug 1;69(2-3):183-8. doi: 10.1016/s0920-9964(03)00176-2. Schizophr Res. 2004. PMID: 15469192
-
Gender aspects in schizophrenia: bridging the border between social and biological psychiatry.Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000;(407):58-62. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2000.00011.x. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000. PMID: 11261642 Review.
-
Generating and testing a causal explanation of the gender difference in age at first onset of schizophrenia.Psychol Med. 1993 Nov;23(4):925-40. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700026398. Psychol Med. 1993. PMID: 8134516 Review.
Cited by
-
Classifying Schizophrenia Cases by Artificial Neural Network Using Japanese Web-Based Survey Data: Case-Control Study.JMIR Form Res. 2023 Nov 15;7:e50193. doi: 10.2196/50193. JMIR Form Res. 2023. PMID: 37966882 Free PMC article.
-
Menstrual Cycle in Schizophrenic Patients: Review with a Case.Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2015 Dec;52(4):417-419. doi: 10.5152/npa.2015.7660. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2015. PMID: 28360750 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic basis of onset age in schizophrenia: evidence and models.Front Genet. 2023 Jun 27;14:1163361. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1163361. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37441552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress in estrogen as an adjunctive therapy for schizophrenia.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Nov 28;49(11):1849-1860. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240289. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 40177768 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Relationship Between Gonadal Hormone Levels and Symptom Severity in Female Patients With Schizophrenia.Alpha Psychiatry. 2021 May 7;22(3):130-135. doi: 10.5455/apd.119468. eCollection 2021 May. Alpha Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 36425447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riecher-Rössler A, Hafner H. Schizophrenia and oestrogens- is there an association? Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1993;242:323–328. - PubMed
-
- Castle DJ, Abel K, Takei N, Murray RM. Gender difference in schizophrenia: hormonal effect or subtypes. Schizophr Bull. 1995;21:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Kulkarni J. Women and schizophrenia: a review. Aust New Zeal J Psychiatry. 1997;31:46–56. - PubMed
-
- Erol A. Kadın üreme yaşamı ve şizofreni. Türk Psikiyatri Dizini. 2005;13:41–44.
-
- Nicole L, Shriqui CL. In: Gender differences in schizophrenia. Nasrallah, editor. Washington: American Psychiatric Press; 1995. pp. 225–243.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources