Guillain-Barre Syndrome in a Patient with Primary Extranodal Intestinal Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma: Paraneoplastic, Drug Induced or Coincidental?
- PMID: 28360641
- PMCID: PMC5353138
- DOI: 10.4274/npa.y7059
Guillain-Barre Syndrome in a Patient with Primary Extranodal Intestinal Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma: Paraneoplastic, Drug Induced or Coincidental?
Abstract
Neurological involvement is observed in 5%-25% of patients with lymphoma being either the first presentation of the disease or emerging during its course. However, Guillain-Barré syndrome is rarely reported. In this article, we present a case with intestinal lymphoma developing Guillain-Barré syndrome during the course of the disease. A 66-year-old male patient with primary extranodal intestinal lymphoma developed quadriparesis, sensory deficits and autonomic dysfunction while receiving chemotherapy. The findings of clinical, electrophysiological and laboratory examinations were consistent with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Guillain-Barré syndrome can potentially be fatal and mimic chemotherapy-induced neurotoxicity, especially in patients with lymphoma, and therefore, must be considered in the differential diagnosis.
Lenfomalı hastaların %5–%25’inde nörolojik tutulum gerek ilk klinik prezentasyon olarak, gerekse hastalık seyri sırasında gözlenebilir. Ancak Guillain Barré sendromu nadiren bidirilmiştir. Bu yazıda intestinal lenfoma seyrinde gelişen bir Guillain Barré sendromu olgusu sunulmuştur. Bilinen primer ekstranodal intestinal lenfoması olan ve kemoterapi alan 66 yaşında bir erkek hastada subakut kuadriparezi, duyu bozukluğu ve otonomik disfonksiyon gelişmiştir. Klinik muayene, elektrofizyolojik incelemeler ve laboratuar bulgularının Guillain-Barré sendromu ile uyumlu olduğu saptanmıştır. Guillain-Barré sendromu ölümcül bir hastalık olma potansiyeline sahiptir ve özellikle lenfoma hastalarında kullanılan kemoterapötik ajanların nörotoksik yan etkilerini taklit edebilir, bu nedenle ayırıcı tanıda gözetilmesi ve tedavisinin hızla başlatılması önemlidir.
Keywords: Guillain-Barré syndrome; lymphoma; neurotoxicity; paraneoplastic syndrome; vincristine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors reported no conflict of interest related to this article. Çıkar çatışması: Yazarlar bu makale ile ilgili olarak herhangi bir çıkar çatışması bildirmemişlerdir.
Figures
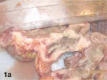
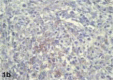
References
-
- Pritchard J, Hughes RA. Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet. 2004;363:2186–2188. - PubMed
-
- Vigliani MC, Magistrello M, Polo P, Mutani R, Chiò A Piemonte and Valle d’Aosta Register for Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Risk of cancer in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS): A population-based study. J Neurol. 2004;251:321–326. - PubMed
-
- Kelly JJ, Karcher DS. Lymphoma and peripheral neuropathy: a clinical review. Muscle Nerve. 2005;31:301–313. - PubMed
-
- Koike H, Tanaka F, Sobue G. Paraneoplastic neuropathy: wide-ranging clinicopathological manifestations. Curr Opin Neurol. 2011;24:504–510. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
