Dexamethasone Pretreatment Alleviates Isoniazid/Lipopolysaccharide Hepatotoxicity: Inhibition of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 28360859
- PMCID: PMC5350150
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00133
Dexamethasone Pretreatment Alleviates Isoniazid/Lipopolysaccharide Hepatotoxicity: Inhibition of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
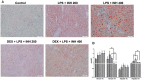
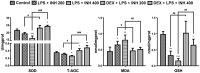
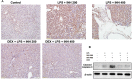
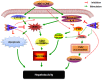
Isoniazid (INH) remains a cornerstone key constitute of the current tuberculosis management strategy, but its hepatotoxic potentiality remains a significant clinical problem. Our previous findings succeed to establish a rat model of INH hepatotoxicity employing the inflammatory stress theory in which non-injurious doses of inflammatory-mediating agent bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) augmented the toxicity of INH that assist to uncover the mechanisms behind INH hepatotoxicity. Following LPS exposure, several inflammatory cells are activated and it is likely that the consequences of this activation rather than direct hepatocellular effects of LPS underlie the ability of LPS to augment toxic responses. In this study, we investigated the potential protective role of the anti-inflammatory agent dexamethasone (DEX), a potent synthetic glucocorticoid, in INH/LPS hepatotoxic rat model. DEX pre-treatment successfully eliminates the components of the inflammatory stress as shown through analysis of blood biochemistry and liver histopathology. DEX potentiated hepatic anti-oxidant mechanisms while serum and hepatic lipid profiles were reduced. However, DEX administration was not able to revoke the principal effects of cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) in INH/LPS-induced liver damage. In conclusion, this study illustrated the DEX-preventive capabilities on INH/LPS-induced hepatotoxicity model through DEX-induced potent anti-inflammatory activity whereas the partial toxicity seen in the model could be attributed to the expression of hepatic CYP2E1. These findings potentiate the clinical applications of DEX co-administration with INH therapy in order to reduce the potential incidences of hepatotoxicity.
Keywords: CYP2E1; dexamethasone; hepatotoxicity; inflammatory stress; isoniazid; lipopolysaccharide; oxidative stress.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Investigating the CYP2E1 Potential Role in the Mechanisms Behind INH/LPS-Induced Hepatotoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Mar 7;9:198. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00198. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29563874 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress, Cytochrome P450 2E1, and Bile Acid Disturbance in Rat Liver Injury Induced by Isoniazid and Lipopolysaccharide Cotreatment.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Aug 22;60(9):5285-93. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00854-16. Print 2016 Sep. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27324775 Free PMC article.
-
Selected pharmaceutical excipient prevent isoniazid and rifampicin induced hepatotoxicity.Curr Drug Metab. 2013 Jul;14(6):720-8. doi: 10.2174/1389200211314060008. Curr Drug Metab. 2013. PMID: 23701163 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical perspectives of isoniazid-induced liver injury.Liver Res. 2021 Feb 11;5(2):45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2021.02.001. eCollection 2021 Jun. Liver Res. 2021. PMID: 39959342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics of isoniazid: The good, the bad, and the alternatives.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019 May;116S:S66-S70. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019. PMID: 31076322 Review.
Cited by
-
Rv0687 a Putative Short-Chain Dehydrogenase Is Required for In Vitro and In Vivo Survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 18;25(14):7862. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147862. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063103 Free PMC article.
-
Icariside Ⅱ, a main compound in Epimedii Folium, induces idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity by enhancing NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Sep;10(9):1619-1633. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.03.006. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 33088683 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective Effect of the Ethanol Extract of Illicium henryi against Acute Liver Injury in Mice Induced by Lipopolysaccharide.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Oct 1;8(10):446. doi: 10.3390/antiox8100446. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31581526 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of a Transgenic Zebrafish Line for In Vivo Assessment of Hepatic Apoptosis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Oct 31;14(11):1117. doi: 10.3390/ph14111117. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832899 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the CYP2E1 Potential Role in the Mechanisms Behind INH/LPS-Induced Hepatotoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Mar 7;9:198. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00198. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29563874 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

