Synthesis and in vitro antitumor activity of (1 E,4 E)-1-aryl-5-(2-((quinazolin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl)-1,4-pentadien-3-one derivatives
- PMID: 28360932
- PMCID: PMC5352699
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-017-0253-9
Synthesis and in vitro antitumor activity of (1 E,4 E)-1-aryl-5-(2-((quinazolin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl)-1,4-pentadien-3-one derivatives
Abstract
Background: Cancer is one of the leading causes of death and only second to heart diseases. Recently, preclinical studies have demonstrated that curcumin had a number of anticancer properties. Thus, we planned to synthesize a series of curcumin analogs to assess their antiproliferation efficacy.
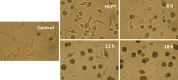
Results: A series of (1E,4E)-1-aryl-5-(2-((quinazolin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl)-1,4-pentadien-3-one derivatives (curcumin analogs) were synthesized and characterized by IR, NMR, and elemental analysis techniques. All of the prepared compounds were screened for antitumor activities against MGC-803, PC3, and Bcap-37 cancer cell lines. A significant inhibition for cancer cells were observed with compound 5f and also less toxic on NIH3T3 normal cells. The mechanism of cell death induced by compound 5f was further investigated by acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining, Hoechst 33,258 staining, TUNEL assay, and flow cytometry cytometry, which revealed that the compound can induce cell apoptosis in MGC-803 cells.
Conclusions: This study suggests that most of the derivatives could inhibit the growth of human cancer cell lines. In addition, compound 5f could induce apoptosis of cancer cells, and it should be subjected to further investigation as a potential anticancer drug candidate.
Keywords: Antitumor activity; Apoptosis; Asymmetric curcumin analogs; MGC-803; Quinazoline derivatives of curcumin; Synthesis.
Figures
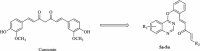




References
-
- Karthikeyan C, Solomon VR, Lee H, Trivedi P. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of some isatin-linked chalcones asnovel anti-breast cancer agents: a molecular hybridization approach. Biomed Prev Nutr. 2013;3:325–330. doi: 10.1016/j.bionut.2013.04.001. - DOI
-
- Fedele P, Marino A, Orlando L, Schiavone P, Nacci A, Sponziello F, Rizzo P, Calvani N, Mazzoni E, Cinefra M, Cinieri S. Efficacy and safety of low-dose metronomic chemotherapy with capecitabine in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:24–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.06.040. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

