Impact of Abbreviated Filgrastim Schedule on Survival and Hematopoietic Recovery after Irradiation in Four Mouse Strains with Different Radiosensitivity
- PMID: 28362168
- PMCID: PMC5539877
- DOI: 10.1667/RR14555.1
Impact of Abbreviated Filgrastim Schedule on Survival and Hematopoietic Recovery after Irradiation in Four Mouse Strains with Different Radiosensitivity
Abstract
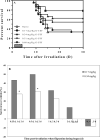
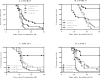
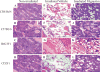
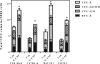
Filgrastim (Neupogen®, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor) is among the few countermeasures recommended for management of patients in the event of lethal total-body irradiation. Despite the plethora of studies using filgrastim as a radiation countermeasure, relatively little is known about the optimal dose schedule of filgrastim to mitigate radiation lethality. We evaluated the efficacy of filgrastim in improving 30-day survival of CD2F1 mice irradiated with a lethal dose (LD70/30) in the AFRRI cobalt-60 facility. We tested different schedules of 1, 3, 5, 10 or 16 once-daily injections of filgrastim initiated one day after irradiation. Time optimization studies with filgrastim treatment were also performed, beginning 6-48 h postirradiation. Maximum survival was observed with 3 daily doses of 0.17 mg/kg filgrastim. Survival efficacy of the 3-day treatment was compared against the conventional 16-day filgrastim treatment after irradiation in four mouse strains with varying radiation sensitivities: C3H/HeN, C57BL/6, B6C3F1 and CD2F1. Blood indices, bone marrow histopathology and colony forming unit assays were also evaluated. Filgrastim significantly increased 30-day survival (P < 0.001) with a 3-day treatment compared to 16-day treatment. Filgrastim did not prevent cytopenia nadirs, but facilitated faster recovery of white blood cells, neutrophils, red blood cells, platelets, lymphocytes and hematocrits in all four strains. Accelerated hematopoietic recovery was also reflected in faster bone marrow reconstitution and significant increase in hematopoietic progenitors (P < 0.001) in all four mouse strains. These data indicate that prompt and abbreviated filgrastim treatment has potential benefit for triage in the event of a radiological incident for treating acute hematopoietic syndrome.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Neulasta or Neupogen on H-ARS and GI-ARS Mortality and Hematopoietic Recovery in Nonhuman Primates After 10-Gy Irradiation With 2.5% Bone Marrow Sparing.Health Phys. 2019 Mar;116(3):339-353. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000000878. Health Phys. 2019. PMID: 30281533 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Radiation Dose and Variation in Neupogen® Initiation Schedule on the Mitigation of Myelosuppression during the Concomitant GI-ARS and H-ARS in a Nonhuman Primate Model of High-dose Exposure with Marrow Sparing.Health Phys. 2015 Nov;109(5):427-39. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000000350. Health Phys. 2015. PMID: 26425903 Free PMC article.
-
The ability of filgrastim to mitigate mortality following LD50/60 total-body irradiation is administration time-dependent.Health Phys. 2014 Jan;106(1):39-47. doi: 10.1097/HP.0b013e3182a4dd2c. Health Phys. 2014. PMID: 24276548 Free PMC article.
-
Use of molecularly-cloned haematopoietic growth factors in persons exposed to acute high-dose, high-dose rate whole-body ionizing radiations.Blood Rev. 2021 Jan;45:100690. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2020.100690. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Blood Rev. 2021. PMID: 32273121 Review.
-
Filgrastim for the treatment of hematopoietic acute radiation syndrome.Drugs Today (Barc). 2015 Sep;51(9):537-48. doi: 10.1358/dot.2015.51.9.2386730. Drugs Today (Barc). 2015. PMID: 26488033 Review.
Cited by
-
Meeting Report: A Poly-Pharmacy Approach to Mitigate Acute Radiation Syndrome.Radiat Res. 2021 Oct 1;196(4):436-446. doi: 10.1667/RADE-21-00048.1. Radiat Res. 2021. PMID: 34237144 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Radiation Countermeasure Development in Radiation Research from 1954 to 2024.Radiat Res. 2024 Aug 1;202(2):420-431. doi: 10.1667/RADE-24-00036.1. Radiat Res. 2024. PMID: 38964743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Treatment Before Radiotherapy Protects Against Radiation-Induced Liver Disease in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 15;12:725084. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.725084. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867327 Free PMC article.
-
PrC-210 Protects against Radiation-Induced Hematopoietic and Intestinal Injury in Mice and Reduces Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jul 13;12(7):1417. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071417. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37507957 Free PMC article.
-
"Longitudinal Fecal Microbiome Study of Total Body Irradiated Mice Treated With Radiation Mitigators Identifies Bacterial Associations With Survival".Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Sep 21;11:715396. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.715396. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34621689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crawford J, Kreisman H, Garewal H, Jones SE, Shoemaker D, Pupa MR, et al. The impact of filgrastim schedule variation on hematopoietic recovery post-chemotherapy. Ann Oncol/ESMO. 1997;8:1117–1124. - PubMed
-
- Smith TJ, Khatcheressian J, Lyman GH, Ozer H, Armitage JO, Balducci L, et al. 2006 update of recommendations for the use of white blood cell growth factors: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:3187–3205. - PubMed
-
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves radiation medical countermeasure. 2015 http://bit.ly/1Tpsbov.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

