Arf GAPs: A family of proteins with disparate functions that converge on a common structure, the integrin adhesion complex
- PMID: 28362242
- PMCID: PMC6548304
- DOI: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1299271
Arf GAPs: A family of proteins with disparate functions that converge on a common structure, the integrin adhesion complex
Abstract
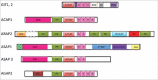
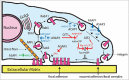
ADP-ribosylation factors (Arfs) are members of the Ras GTPase superfamily. The function of Arfs is dependent on GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) and guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), which allow Arfs to cycle between the GDP-bound and GTP-bound forms. Arf GAPs have been shown to be present in integrin adhesion complexes, which include focal adhesions. Integrin adhesion complexes are composed of integrins, scaffolding proteins and signaling proteins and regulate cell proliferation, survival, differentiation and migration. Understanding the role of Arf GAPs in the regulation of integrin adhesion complexes is relevant to understanding normal physiology and cancer. In this review, we will discuss the contribution of the Arf GAP family members to the regulation of integrin adhesion complexes, examining the diverse mechanisms by which they control integrin adhesion complex formation, maturation and dissolution. GIT1 and ARAP2 serve as GAPs for Arf6, regulating Rac1 and other effectors by mechanisms still being defined. In contrast, GIT2 regulates Rac1 independent of Arf6. AGAP2 binds to and regulates focal adhesion kinase (FAK). ARAP2 and ACAP1, both Arf6 GAPs, regulate membrane trafficking of integrins through different endocytic pathways, exerting opposite effects on focal adhesions. ASAP1 not only regulates actin cytoskeleton remodeling through its interaction with nonmuscle myosin 2A, but is also important in integrin recycling. These examples illustrate the diversity and versatility of Arf GAPs as regulators of integrin adhesion complex structure and function.
Keywords: ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein; ADP-ribosylation factors; ARAP2; ASAP1; GIT1/2; Integrin adhesion complex.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Arf6 GTPase-activating proteins ARAP2 and ACAP1 define distinct endosomal compartments that regulate integrin α5β1 traffic.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 31;289(44):30237-30248. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.596155. Epub 2014 Sep 15. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25225293 Free PMC article.
-
Arf GAPs as Regulators of the Actin Cytoskeleton-An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 21;20(2):442. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020442. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30669557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ARAP2 signals through Arf6 and Rac1 to control focal adhesion morphology.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 22;288(8):5849-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.415778. Epub 2013 Jan 7. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23295182 Free PMC article.
-
ACAPs are arf6 GTPase-activating proteins that function in the cell periphery.J Cell Biol. 2000 Oct 30;151(3):627-38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.3.627. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11062263 Free PMC article.
-
Arf proteins in cancer cell migration.Small GTPases. 2016 Oct;7(4):270-282. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1228792. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Small GTPases. 2016. PMID: 27589148 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of candidate mediators of chemoresponse in breast cancer through therapy-driven selection of somatic variants.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Oct;183(3):607-616. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05836-7. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32734521 Free PMC article.
-
Arl13b Regulates Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Controlling Integrin-Mediated Signaling.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 29;11(10):1461. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101461. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31569511 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of G proteins and their GTPase-activating proteins in platelets.Biosci Rep. 2024 May 29;44(5):BSR20231420. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231420. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38808367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Protein Biomarkers for Invasive Lung Cancer.Curr Oncol. 2024 Aug 23;31(9):4818-4854. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31090360. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39329988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ARF GTPases and their GEFs and GAPs: concepts and challenges.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 May 15;30(11):1249-1271. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-12-0820. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31084567 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huttenlocher A, Horwitz AR. Integrins in Cell Migration. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2011; 3:a005074; PMID:21885598; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a005074 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moreno-Layseca P, Streuli CH. Signalling pathways linking integrins with cell cycle progression. Matrix Biol 2014; 34:144-53; PMID:24184828; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2013.10.011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Streuli CH. Integrins and cell-fate determination. J Cell Sci 2009; 122:171-7; PMID:19118209; http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/jcs.018945 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guo WJ, Giancotti FG. Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5:816-26; PMID:15459662; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm1490 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hehlgans S, Haase M, Cordes N. Signalling via integrins: Implications for cell survival and anticancer strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007; 1775:163-80; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2006.09.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
