Identification and validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR studies in long yellow daylily, Hemerocallis citrina Borani
- PMID: 28362875
- PMCID: PMC5376306
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174933
Identification and validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR studies in long yellow daylily, Hemerocallis citrina Borani
Abstract
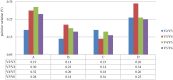
Gene expression analysis using reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) requires the use of reference gene(s) in the target species. The long yellow daylily, Hemerocallis citrina Baroni. is rich in beneficial secondary metabolites and is considered as a functional vegetable. It is widely cultivated and consumed in East Asian countries. However, reference genes for use in RT-qPCR in H. citrina are not available. In the present study, six potential reference genes, actin (ACT), AP-4 complex subunit (AP4), tubulin (TUB), ubiquitin (UBQ), 18S and 60S ribosomal RNA, were selected and their expression stability in different developmental stages, organs and accessions was evaluated using four statistical software packages (geNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper, and RefFinder). For commercial flower buds of different landraces, the combination of 60S, TUB, and AP4 was appropriate whereas ACT and 60S was suitable for normalization of different organs. In addition, AP4 exhibited the most stable expression in flower buds among different developmental stages. UBQ was less stable than the other reference genes under the experimental conditions except under different organs was 18S. The relative expression levels of two genes, primary-amine oxidase (HcAOC3) and tyrosine aminotransferase (HcTAT) which play important roles in alkaloid biosynthesis were also examined in different organs of the 'Datong' landrace, which further confirmed the results of selected reference genes. This is the first report to evaluate the stability of reference genes in the long yellow daylily that can serve as a foundation for RT-qPCR analysis of gene expression in this species.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Hotta M, Ito M, Okada I. Differentiation and species relationships of island population of Hemerocallis around Kyushu, Japan In: Hara H (ed) Origin and evolution of diversity in plants and plant communities. Academia Scientific Book Inc., 1985; pp:18–30.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

