Race, Serum Potassium, and Associations With ESRD and Mortality
- PMID: 28363732
- PMCID: PMC5526716
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.01.044
Race, Serum Potassium, and Associations With ESRD and Mortality
Abstract
Background: Recent studies suggest that potassium levels may differ by race. The basis for these differences and whether associations between potassium levels and adverse outcomes differ by race are unknown.
Study design: Observational study.
Setting & participants: Associations between race and potassium level and the interaction of race and potassium level with outcomes were investigated in the Racial and Cardiovascular Risk Anomalies in Chronic Kidney Disease (RCAV) Study, a cohort of US veterans (N=2,662,462). Associations between African ancestry and potassium level were investigated in African Americans in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study (N=3,450).
Predictors: Race (African American vs non-African American and percent African ancestry) for cross-sectional analysis; serum potassium level for longitudinal analysis.
Outcomes: Potassium level for cross-sectional analysis; mortality and end-stage renal disease for longitudinal analysis.
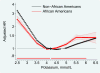
Results: The RCAV cohort was 18% African American (N=470,985). Potassium levels on average were 0.162mmol/L lower in African Americans compared with non-African Americans, with differences persisting after adjustment for demographics, comorbid conditions, and potassium-altering medication use. In the ARIC Study, higher African ancestry was related to lower potassium levels (-0.027mmol/L per each 10% African ancestry). In both race groups, higher and lower potassium levels were associated with mortality. Compared to potassium level of 4.2mmol/L, mortality risk associated with lower potassium levels was lower in African Americans versus non-African Americans, whereas mortality risk associated with higher levels was slightly greater. Risk relationships between potassium and end-stage renal disease were weaker, with no difference by race.
Limitations: No data for potassium intake.
Conclusions: African Americans had slightly lower serum potassium levels than non-African Americans. Consistent associations between potassium levels and percent African ancestry may suggest a genetic component to these differences. Higher and lower serum potassium levels were associated with mortality in both racial groups.
Keywords: African American; African ancestry; Race; end-stage renal disease (ESRD); genetic risk factor; hyperkalemia; hypokalemia; kidney disease; mortality; racial differences; serum potassium.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Mattsson N, Sadjadieh G, Kumarathurai P, Nielsen OW, Køber L, Sajadieh A. Ambulatory cardiac arrhythmias in relation to mild hypokalaemia and prognosis in community dwelling middle-aged and elderly subjects. Europace. 2015:euv204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK106515/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK108803/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK092287/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

