A Phase Ib Dose-Escalation Study of Encorafenib and Cetuximab with or without Alpelisib in Metastatic BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 28363909
- PMCID: PMC5546207
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0795
A Phase Ib Dose-Escalation Study of Encorafenib and Cetuximab with or without Alpelisib in Metastatic BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
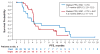
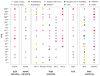
Preclinical evidence suggests that concomitant BRAF and EGFR inhibition leads to sustained suppression of MAPK signaling and suppressed tumor growth in BRAFV600E colorectal cancer models. Patients with refractory BRAFV600-mutant metastatic CRC (mCRC) were treated with a selective RAF kinase inhibitor (encorafenib) plus a monoclonal antibody targeting EGFR (cetuximab), with (n = 28) or without (n = 26) a PI3Kα inhibitor (alpelisib). The primary objective was to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) or a recommended phase II dose. Dose-limiting toxicities were reported in 3 patients receiving dual treatment and 2 patients receiving triple treatment. The MTD was not reached for either group and the phase II doses were selected as 200 mg encorafenib (both groups) and 300 mg alpelisib. Combinations of cetuximab and encorafenib showed promising clinical activity and tolerability in patients with BRAF-mutant mCRC; confirmed overall response rates of 19% and 18% were observed and median progression-free survival was 3.7 and 4.2 months for the dual- and triple-therapy groups, respectively.Significance: Herein, we demonstrate that dual- (encorafenib plus cetuximab) and triple- (encorafenib plus cetuximab and alpelisib) combination treatments are tolerable and provide promising clinical activity in the difficult-to-treat patient population with BRAF-mutant mCRC. Cancer Discov; 7(6); 610-9. ©2017 AACR.See related commentary by Sundar et al., p. 558This article is highlighted in the In This Issue feature, p. 539.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
JT reports compensation for an advisory role from Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Chugai, Lilly, MSD, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Symphogen, Takeda and Taiho. MS reports compensation for advisory boards from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Novartis; compensation for CME presentations from Alexion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi and research grants (to institution) from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis. TY reports research grants (to institution) from Daiichi Sankyo, Taiho, Bayer Yakuhin, Lilly, Pfizer, Yakult Honsha, Chugai, Dainippon Sumitomo; personal fees from Merck Serono, Chugai, Takeda. ML reports research grants (to institution) from Astellas, Johnson & Johnson and Sanofi. JEF reports current employment with Novartis and personal fees from N-of-One Therapeutics, Merrimack Pharmaceuticals. SS reports research grants (to institution) from Novartis and compensation for an advisory role from Novartis. RY reports research grants (to institution) from Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Genentech and compensation for advisory boards from GlaxoSmithKline. ZW reports research grants (to institution) from Novartis. EA, AC, SJ, ET and TD report employment with Novartis. KM reports employment with Array BioPharma Inc. RVG, EE, JCB, AS, J-PD, YY, FE, H-J L and JHMS have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Comment in
-
Targeting BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancer: Progress in Combination Strategies.Cancer Discov. 2017 Jun;7(6):558-560. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0087. Cancer Discov. 2017. PMID: 28576843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- De Roock W, Biesmans B, De Schutter J, Tejpar S. Clinical biomarkers in oncology: focus on colorectal cancer. Mol Diagn Ther. 2009;13(2):103–14. - PubMed
-
- Rizzo S, Bronte G, Fanale D, Corsini L, Silvestris N, Santini D, et al. Prognostic vs predictive molecular biomarkers in colorectal cancer: is KRAS and BRAF wild type status required for anti-EGFR therapy? Cancer Treat Rev. 2010 Nov;36( Suppl 3):S56–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

