Distinct Patterns of Gene Gain and Loss: Diverse Evolutionary Modes of NBS-Encoding Genes in Three Solanaceae Crop Species
- PMID: 28364035
- PMCID: PMC5427506
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.117.040485
Distinct Patterns of Gene Gain and Loss: Diverse Evolutionary Modes of NBS-Encoding Genes in Three Solanaceae Crop Species
Abstract
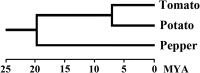
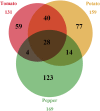
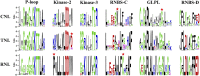
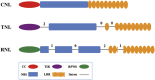
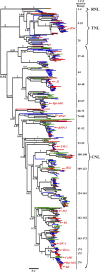
Plant resistance conferred by nucleotide binding site (NBS)-encoding resistance genes plays a key role in the defense against various pathogens throughout the entire plant life cycle. However, comparative analyses for the systematic evaluation and determination of the evolutionary modes of NBS-encoding genes among Solanaceae species are rare. In this study, 447, 255, and 306 NBS-encoding genes were identified from the genomes of potato, tomato, and pepper, respectively. These genes usually clustered as tandem arrays on chromosomes; few existed as singletons. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that three subclasses [TNLs (TIR-NBS-LRR), CNLs (CC-NBS-LRR), and RNLs (RPW8-NBS-LRR)] each formed a monophyletic clade and were distinguished by unique exon/intron structures and amino acid motif sequences. By comparing phylogenetic and systematic relationships, we inferred that the NBS-encoding genes in the present genomes of potato, tomato, and pepper were derived from 150 CNL, 22 TNL, and 4 RNL ancestral genes, and underwent independent gene loss and duplication events after speciation. The NBS-encoding genes therefore exhibit diverse and dynamic evolutionary patterns in the three Solanaceae species, giving rise to the discrepant gene numbers observed today. Potato shows a "consistent expansion" pattern, tomato exhibits a pattern of "first expansion and then contraction," and pepper presents a "shrinking" pattern. The earlier expansion of CNLs in the common ancestor led to the dominance of this subclass in gene numbers. However, RNLs remained at low copy numbers due to their specific functions. Along the evolutionary process of NBS-encoding genes in Solanaceae, species-specific tandem duplications contributed the most to gene expansions.
Keywords: NBS-encoding genes; Solanaceae; evolutionary pattern; phylogenetic relationship.
Copyright © 2017 Qian et al.
Figures

References
-
- Andolfo G., Sanseverino W., Rombauts S., Van de Peer Y., Bradeen J. M., et al. , 2013. Overview of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) candidate pathogen recognition genes reveals important Solanum R locus dynamics. New Phytol. 197(1): 223–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
