Improved Long-term Outcomes of Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease Receiving Proactive Compared With Reactive Monitoring of Serum Concentrations of Infliximab
- PMID: 28365486
- PMCID: PMC5605429
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.03.031
Improved Long-term Outcomes of Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease Receiving Proactive Compared With Reactive Monitoring of Serum Concentrations of Infliximab
Abstract
Background & aims: Monitoring serum concentrations of tumor necrosis factor antagonists in patients receiving these drugs as treatment for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), also called therapeutic drug monitoring, is performed either after patient loss of response (reactive drug monitoring) or in patients in clinical remission in which the drug is titrated to a target concentration (proactive drug monitoring). We compared long-term outcomes of patients with IBD undergoing proactive vs reactive monitoring of serum concentrations of infliximab.
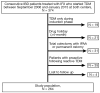
Methods: We performed a multicenter, retrospective study of 264 consecutive patients with IBD (167 with Crohn's disease) receiving infliximab maintenance therapy. The subjects received proactive (n = 130) or reactive (n = 134) drug monitoring, based on measurements of first infliximab concentration and antibodies to infliximab, from September 2006 to January 2015; they were followed through December 2015 (median time of 2.4 years). We analyzed time to treatment failure, first IBD-related surgery or hospitalization, serious infusion reaction, and detection of antibodies to infliximab. Treatment failure was defined as drug discontinuation for loss of response or serious adverse event, or need for surgery.
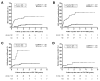
Results: Multiple Cox regression analysis independently associated proactive drug monitoring, compared with reactive monitoring, with reduced risk for treatment failure (hazard ratio [HR], 0.16; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.09-0.27; P < .001), IBD-related surgery (HR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.11-0.80; P = .017), IBD-related hospitalization (HR, 0.16; 95% CI, 0.07-0.33; P < .001), antibodies to infliximab (HR, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.07-0.84; P = .025), and serious infusion reaction (HR, 0.17; 95% CI, 0.04-0.78; P = .023).
Conclusions: In a retrospective analysis of patients with IBD receiving proactive vs reactive monitoring of serum concentration of infliximab, proactive monitoring was associated with better clinical outcomes, including greater drug durability, less need for IBD-related surgery or hospitalization, and lower risk of antibodies to infliximab or serious infusion reactions.
Keywords: CD; Immunogenicity; Monitoring Therapy; Ulcerative Colitis.
Copyright © 2017 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose the following: Byron P. Vaughn receives research support from Takeda and Genentech and has received compensation from Janssen and AbbVie for speaking and advisory boards. Mark T. Osterman received consultancy fees from Janssen, AbbVie, UCB, Takeda, Pfizer, and Lycera, and received research grant support from UCB. Adam S. Cheifetz received consultancy fees from AbbVie, Janssen, UCB, Takeda, Prometheus, and Pfizer. The remaining authors disclose no conflicts of interest.
Figures
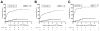

Comment in
-
Proactive and Reactive Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Biologic Therapies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Are Complementary, Not Mutually Exclusive.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Apr;16(4):597-598. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.11.033. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29555230 No abstract available.
-
Reply.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Apr;16(4):598-599. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.12.030. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29555231 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ben-Horin S, Chowers Y. Loss of response to anti-TNF treatments in Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;33:987–995. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

