Statin Treatment and Clinical Outcomes of Heart Failure Among Africans: An Inverse Probability Treatment Weighted Analysis
- PMID: 28365564
- PMCID: PMC5532994
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004706
Statin Treatment and Clinical Outcomes of Heart Failure Among Africans: An Inverse Probability Treatment Weighted Analysis
Abstract
Background: Randomized control trials of statins have not demonstrated significant benefits in outcomes of heart failure (HF). However, randomized control trials may not always be generalizable. The aim was to determine whether statin and statin type-lipophilic or -hydrophilic improve long-term outcomes in Africans with HF.
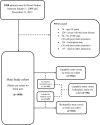
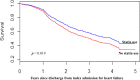
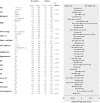
Methods and results: This was a retrospective longitudinal study of HF patients aged ≥18 years hospitalized at a tertiary healthcare center between January 1, 2009 and December 31, 2013 in Ghana. Patients were eligible if they were discharged from first admission for HF (index admission) and followed up to time of all-cause, cardiovascular, and HF mortality or end of study. Multivariable time-dependent Cox model and inverse-probability-of-treatment weighting of marginal structural model were used to estimate associations between statin treatment and outcomes. Adjusted hazard ratios were also estimated for lipophilic and hydrophilic statin compared with no statin use. The study included 1488 patients (mean age 60.3±14.2 years) with 9306 person-years of observation. Using the time-dependent Cox model, the 5-year adjusted hazard ratios with 95% CI for statin treatment on all-cause, cardiovascular, and HF mortality were 0.68 (0.55-0.83), 0.67 (0.54-0.82), and 0.63 (0.51-0.79), respectively. Use of inverse-probability-of-treatment weighting resulted in estimates of 0.79 (0.65-0.96), 0.77 (0.63-0.96), and 0.77 (0.61-0.95) for statin treatment on all-cause, cardiovascular, and HF mortality, respectively, compared with no statin use.
Conclusions: Among Africans with HF, statin treatment was associated with significant reduction in mortality.
Keywords: Africans; inverse probability treatment weighting; outcome; race and ethnicity; statin therapy.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipophilic Statin Versus Rosuvastatin (Hydrophilic) Treatment for Heart Failure: a Meta-Analysis and Adjusted Indirect Comparison of Randomised Trials.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2016 Apr;30(2):177-88. doi: 10.1007/s10557-015-6636-z. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2016. PMID: 26780905
-
Impact of Different Types of Statins on Clinical Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized for Ischemic Heart Failure.Med Arch. 2018 Dec;72(6):401-405. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2018.72.401-405. Med Arch. 2018. PMID: 30814769 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes of statin dose, class, and use intensity on primary prevention of cardiovascular mortality: a national T2DM cohort study.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2023 May;79(5):687-700. doi: 10.1007/s00228-023-03488-2. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37010535
-
Statin use associated with a reduced risk of pneumonia requiring hospitalization in patients with myocardial infarction: a nested case-control study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2016 Jan 28;16:24. doi: 10.1186/s12872-016-0202-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2016. PMID: 26823081 Free PMC article.
-
Association of statin use and clinical outcomes in heart failure patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Oct 31;18(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1135-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31672151 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Simvastatin Combined with Resistance Training Improves Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure by Modulating Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and the Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Signaling Pathways.Cardiovasc Ther. 2022 Mar 12;2022:8430733. doi: 10.1155/2022/8430733. eCollection 2022. Cardiovasc Ther. 2022. PMID: 35356068 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Statin Use and Cancer Incidence in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Network Meta-Analysis.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018 Sep 4;2018:8620682. doi: 10.1155/2018/8620682. eCollection 2018. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30254671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and Predictors of Statin Treatment Among Patients With Chronic Heart Failure at a Tertiary-Care Center in Thailand.Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2019 Jun 10;13:1179546819855656. doi: 10.1177/1179546819855656. eCollection 2019. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31217695 Free PMC article.
-
Association is not causation: treatment effects cannot be estimated from observational data in heart failure.Eur Heart J. 2018 Oct 1;39(37):3417-3438. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy407. Eur Heart J. 2018. PMID: 30085087 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Dyslipidaemia Using an Algorithm of Lipid Profile Measures among Newly Diagnosed Type II Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study at Dormaa Presbyterian Hospital, Ghana.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Jul 21;55(7):392. doi: 10.3390/medicina55070392. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31330902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Callender T, Woodward M, Roth G, Farzadfar F, Lemarie JC, Gicquel S, Atherton J, Rahimzadeh S, Ghaziani M, Shaikh M, Bennett D, Patel A, Lam CS, Sliwa K, Barretto A, Siswanto BB, Diaz A, Herpin D, Krum H, Eliasz T, Forbes A, Kiszely A, Khosla R, Petrinic T, Praveen D, Shrivastava R, Xin D, MacMahon S, McMurray J, Rahimi K. Heart failure care in low‐ and middle‐income countries: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. PLoS Med. 2014;11:e1001699. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet. 1994;344:1383–1389. - PubMed
-
- Prevention of cardiovascular events and death with pravastatin in patients with coronary heart disease and a broad range of initial cholesterol levels. The Long‐Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischaemic Disease (LIPID) Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1349–1357. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

