Decreased Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Incident Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) in Recent Years: Dawn of a New Era in Cardiovascular Disease in RA?
- PMID: 28365576
- PMCID: PMC5457313
- DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.161154
Decreased Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Incident Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) in Recent Years: Dawn of a New Era in Cardiovascular Disease in RA?
Abstract
Objective: To assess trends in cardiovascular (CV) mortality in patients with incident rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in 2000-07 versus the previous decades, compared with non-RA subjects.
Methods: The study population consisted of Olmsted County, Minnesota, USA residents with incident RA (age ≥ 18 yrs, 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria was met in 1980-2007) and non-RA subjects from the same underlying population with similar age, sex, and calendar year of index. All subjects were followed until death, migration, or December 31, 2014. Followup was truncated for comparability. Aalen-Johansen methods were used to estimate CV mortality rates, adjusting for competing risk of other causes. Cox proportional hazards models were used to compare CV mortality by decade.
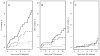
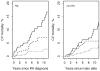
Results: The study included 813 patients with RA and 813 non-RA subjects (mean age 55.9 yrs; 68% women for both groups). Patients with incident RA in 2000-07 had markedly lower 10-year overall CV mortality (2.7%, 95% CI 0.6-4.9%) and coronary heart disease (CHD) mortality (1.1%, 95% CI 0.0-2.7%) than patients diagnosed in 1990-99 (7.1%, 95% CI 3.9-10.1% and 4.5%, 95% CI 1.9-7.1%, respectively; HR for overall CV death: 0.43, 95% CI 0.19-0.94; CHD death: HR 0.21, 95% CI 0.05-0.95). This improvement in CV mortality persisted after accounting for CV risk factors. Ten-year overall CV mortality and CHD mortality in 2000-07 RA incidence cohort was similar to non-RA subjects (p = 0.95 and p = 0.79, respectively).
Conclusion: Our findings suggest significantly improved overall CV mortality, particularly CHD mortality, in patients with RA in recent years. Further studies are needed to examine the reasons for this improvement.
Keywords: CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE; CORONARY HEART DISEASE; MORTALITY; RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS.
Figures
References
-
- Avina-Zubieta JA, Choi HK, Sadatsafavi M, Etminan M, Esdaile JM, Lacaille D. Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:1690–7. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F, Michaud K. The risk of myocardial infarction and pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic myocardial infarction predictors in rheumatoid arthritis: a cohort and nested case-control analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:2612–21. - PubMed
-
- Masuda H, Miyazaki T, Shimada K, Tamura N, Matsudaira R, Yoshihara T, et al. Disease duration and severity impacts on long-term cardiovascular events in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Cardiol. 2014;64:366–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
