Management of acute intracerebral haemorrhage - an update
- PMID: 28365631
- PMCID: PMC6297624
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmedicine.17-2-166
Management of acute intracerebral haemorrhage - an update
Abstract
Managing acute intracerebral haemorrhage is a challenging task for physicians. Evidence shows that outcome can be improved with admission to an acute stroke unit and active care, including urgent reversal of anticoagulant effects and, potentially, intensive blood pressure reduction. Nevertheless, many management issues remain controversial, including the use of haemostatic therapy, selection of patients for neurosurgery and neurocritical care, the extent of investigations for underlying causes and the benefit versus risk of restarting antithrombotic therapy after an episode of intracerebral haemorrhage.
Keywords: Antithrombotic; blood pressure; intracerebral haemorrhage; management; neurosurgery; stroke.
© Royal College of Physicians 2017. All rights reserved.
Figures
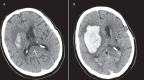
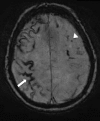
References
-
- van Asch CJ. Luitse MJ. Rinkel GJ, et al. Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:167–76. - PubMed
-
- Demchuk AM. Dowlatshahi D. Rodriguez-Luna D, et al. Prediction of haematoma growth and outcome in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage using the CT-angiography spot sign (PREDICT): a prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11:307–14. - PubMed
-
- Cordonnier C. Klijn CJ. van Beijnum J. Al-Shahi Salman R. Radiological investigation of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: systematic review and trinational survey. Stroke. 2010;41:685–90. - PubMed
-
- Wilson D. Adams ME. Robertson F. Murphy M. Werring DJ. Investigating intracerebral haemorrhage. BMJ. 2015;350:h2484. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

