A path to precision in the ICU
- PMID: 28366166
- PMCID: PMC5376689
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1653-x
A path to precision in the ICU
Abstract
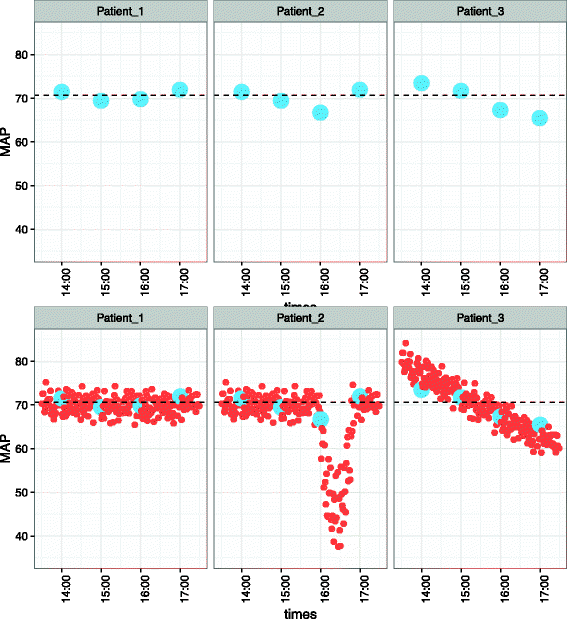
Precision medicine is increasingly touted as a groundbreaking new paradigm in biomedicine. In the ICU, the complexity and ambiguity of critical illness syndromes have been identified as fundamental justifications for the adoption of a precision approach to research and practice. Inherently protean diseases states such as sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome have manifestations that are physiologically and anatomically diffuse, and that fluctuate over short periods of time. This leads to considerable heterogeneity among patients, and conditions in which a "one size fits all" approach to therapy can lead to widely divergent results. Current ICU therapy can thus be seen as imprecise, with the potential to realize substantial gains from the adoption of precision medicine approaches. A number of challenges still face the development and adoption of precision critical care, a transition that may occur incrementally rather than wholesale. This article describes a few concrete approaches to addressing these challenges.First, novel clinical trial designs, including registry randomized controlled trials and platform trials, suggest ways in which conventional trials can be adapted to better accommodate the physiologic heterogeneity of critical illness. Second, beyond the "omics" technologies already synonymous with precision medicine, the data-rich environment of the ICU can generate complex physiologic signatures that could fuel precision-minded research and practice. Third, the role of computing infrastructure and modern informatics methods will be central to the pursuit of precision medicine in the ICU, necessitating close collaboration with data scientists. As work toward precision critical care continues, small proof-of-concept studies may prove useful in highlighting the potential of this approach.
Keywords: Biomedical informatics; Clinical trials; Critical care; Genomics; Intensive care unit; Personalized medicine; Precision health; Precision medicine.
Figures
Comment in
-
Systematic assessment of advanced respiratory physiology: precision medicine entering real-life ICU?Crit Care. 2017 Jun 16;21(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1720-3. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28623930 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hudson K, Lifton R, Patrick-Lake B, Burchard EG, Coles T, Collins R, Conrad A, Desmond-Hellmann S, Dishman E, Giusti K, et al. The precision medicine initiative cohort program: building a research foundation for 21st century medicine. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health; 2105. https://acd.od.nih.gov/reports/DRAFT-PMI-WG-Report-9-11-2015-508.pdf. Accessed 13 Mar 2017
-
- Kaufman DJ, Baker R, Milner LC, Devaney S, Hudson KL. A survey of U.S adults’ opinions about conduct of a Nationwide Precision Medicine Initiative® cohort study of genes and environment. Hernandez Montoya AR, editor. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0160461–14. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160461. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antman EM, Loscalzo J. Precision medicine in cardiology. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016;13:591-602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

