Stem cells and necrotizing enterocolitis: A direct comparison of the efficacy of multiple types of stem cells
- PMID: 28366560
- PMCID: PMC5467690
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.03.028
Stem cells and necrotizing enterocolitis: A direct comparison of the efficacy of multiple types of stem cells
Abstract
Purpose: Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a leading cause of gastrointestinal morbidity and mortality in premature infants. While studies have shown potential for stem cell (SC) therapy in experimental NEC, no study has compared different SC side-by-side. Our purpose was to determine whether one type of SC may more effectively treat NEC than others.
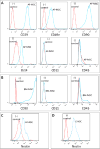
Methods: Four SC were compared: (1) amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal SC (AF-MSC); (2) amniotic fluid-derived neural SC (AF-NSC); (3) bone marrow-derived mesenchymal SC (BM-MSC); and (4) neonatal enteric neural SC (E-NSC). Using an established rat model of NEC, pups delivered prematurely received an intraperitoneal injection of SC. Control pups were injected with PBS. Additional controls were breast-fed by surrogates and not subjected to experimental NEC. Intestinal tissue was graded histologically.
Results: NEC incidence was: PBS, 61.3%; breast-fed unstressed, 0%; AF-MSC, 19.1%; BM-MSC, 22.9%; AF-NSC, 18.9%; E-NSC 22.2%. All groups demonstrated statistical significance (p<0.05) compared to controls, and there was no difference between SC groups.
Conclusion: All four SC groups reduced the incidence and severity of experimental NEC equivalently. AF-MSC may be preferable because of availability of AF at delivery and ease of expansion, increasing potential for clinical translation.
Level of evidence: V (Animal study).
Keywords: Amniotic fluid; Mesenchymal; NEC; Necrotizing enterocolitis; Neural stem cells; Stem cells.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Eaton S, Zani A, Pierro A, De Coppi P. Stem cells as a potential therapy for necrotizing enterocolitis. Expert opinion on biological therapy. 2013;13(12):1683–9. Epub 2013/10/25. - PubMed
-
- Zani A, Cananzi M, Lauriti G, Fascetti-Leon F, Wells J, Siow B, et al. Amniotic fluid stem cells prevent development of ascites in a neonatal rat model of necrotizing enterocolitis. European journal of pediatric surgery: official journal of Austrian Association of Pediatric Surgery [et al] = Zeitschrift fur Kinderchirurgie. 2014;24(1):57–60. Epub 2013/07/16. - PubMed
-
- Tayman C, Uckan D, Kilic E, Ulus AT, Tonbul A, Murat Hirfanoglu I, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in necrotizing enterocolitis: a rat study. Pediatric research. 2011;70(5):489–94. Epub 2011/07/21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

