Spt5 Plays Vital Roles in the Control of Sense and Antisense Transcription Elongation
- PMID: 28366642
- PMCID: PMC5394798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.023
Spt5 Plays Vital Roles in the Control of Sense and Antisense Transcription Elongation
Abstract
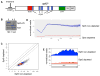
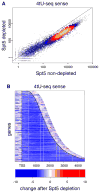
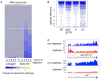
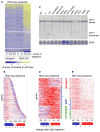
Spt5 is an essential and conserved factor that functions in transcription and co-transcriptional processes. However, many aspects of the requirement for Spt5 in transcription are poorly understood. We have analyzed the consequences of Spt5 depletion in Schizosaccharomyces pombe using four genome-wide approaches. Our results demonstrate that Spt5 is crucial for a normal rate of RNA synthesis and distribution of RNAPII over transcription units. In the absence of Spt5, RNAPII localization changes dramatically, with reduced levels and a relative accumulation over the first ∼500 bp, suggesting that Spt5 is required for transcription past a barrier. Spt5 depletion also results in widespread antisense transcription initiating within this barrier region. Deletions of this region alter the distribution of RNAPII on the sense strand, suggesting that the barrier observed after Spt5 depletion is normally a site at which Spt5 stimulates elongation. Our results reveal a global requirement for Spt5 in transcription elongation.
Keywords: Spt5; antisense transcription; convergent antisense transcription; transcription elongation.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl KE. Current protocols in molecular biology. Green Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience; New York, NY: 1991.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

