A Metabolic Function for Phospholipid and Histone Methylation
- PMID: 28366644
- PMCID: PMC5482412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.026
A Metabolic Function for Phospholipid and Histone Methylation
Abstract
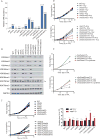
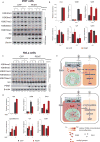
S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) is the methyl donor for biological methylation modifications that regulate protein and nucleic acid functions. Here, we show that methylation of a phospholipid, phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), is a major consumer of SAM. The induction of phospholipid biosynthetic genes is accompanied by induction of the enzyme that hydrolyzes S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH), a product and inhibitor of methyltransferases. Beyond its function for the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine (PC), the methylation of PE facilitates the turnover of SAM for the synthesis of cysteine and glutathione through transsulfuration. Strikingly, cells that lack PE methylation accumulate SAM, which leads to hypermethylation of histones and the major phosphatase PP2A, dependency on cysteine, and sensitivity to oxidative stress. Without PE methylation, particular sites on histones then become methyl sinks to enable the conversion of SAM to SAH. These findings reveal an unforeseen metabolic function for phospholipid and histone methylation intrinsic to the life of a cell.
Keywords: H3K36; S-adenosylmethionine; cysteine; epigenetics; glutathione; histone methylation; methyltransferase; phospholipids; transsulfuration.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

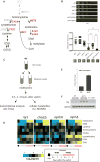
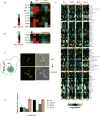
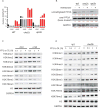
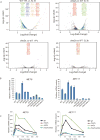
Comment in
-
Metabolism: Methyl groups sink into phospholipids and histones.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Jun;18(6):342-343. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.44. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28400609 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bremer J, Greenberg DM. Methyl transfering enzyme system of microsomes in the biosynthesis of lecithin (phosphatidylcholine) Biochimica et biophysica acta. 1961;46:205–216.
-
- Brosnan JT, Brosnan ME. The sulfur-containing amino acids: an overview. The Journal of nutrition. 2006;136:1636S–1640S. - PubMed
-
- Cai L, Tu BP. Driving the cell cycle through metabolism. Annual review of cell and developmental biology. 2012;28:59–87. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

