Focal adhesion kinases crucially regulate TGFβ-induced migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells via Src kinase and E-cadherin
- PMID: 28367061
- PMCID: PMC5370070
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S122463
Focal adhesion kinases crucially regulate TGFβ-induced migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells via Src kinase and E-cadherin
Abstract
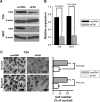
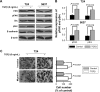
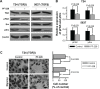
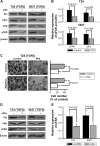
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinase that is triggered off by special extracellular signals such as some growth factors and integrins. FAK is found in cell-matrix attachment sites and implicated in cell migration, invasion, movement, gene expression, survival and apoptosis. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether FAK plays a role in invasion and migration of bladder cancer cells. Using an FAK-specific small interfering RNA (siRNA) and an FAK inhibitor PF-228, we found that inhibition of FAK tyrosine phosphorylation or knockdown of FAK suppressed invasion and migration of bladder cancer cells. Src is an important mediator of FAK-regulated migratory and invasive activity. Tyrosine phosphorylation of Src and FAK is mutually dependent and plays a key role in transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ)-induced invasion and migration. E-cadherin acts downstream of FAK and is a critical negative regulator in FAK-regulated invasion and migration of bladder cancer cells. These findings imply that FAK is involved in oncogenic signaling of invasion and migration, which can be a novel therapeutic target to treat patients with bladder cancer.
Keywords: E-cadherin; Src kinase; bladder cancer; focal adhesion kinase; migration/invasion; transforming growth factor beta.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase induces apoptosis in bladder cancer cells via Src and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2015 Nov;10(5):1725-1731. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2745. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26640543 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesion kinase signaling is necessary for the Cyclosporin A-enhanced migration and invasion of human trophoblast cells.Placenta. 2012 Sep;33(9):704-11. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2012.06.007. Epub 2012 Jul 4. Placenta. 2012. PMID: 22766276
-
TGFβ induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition of thyroid cancer cells by both the BRAF/MEK/ERK and Src/FAK pathways.Mol Carcinog. 2016 Nov;55(11):1639-1654. doi: 10.1002/mc.22415. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Mol Carcinog. 2016. PMID: 26392228
-
The focal adhesion kinase--a regulator of cell migration and invasion.IUBMB Life. 2002 Feb;53(2):115-9. doi: 10.1080/15216540211470. IUBMB Life. 2002. PMID: 12049193 Review.
-
Focal adhesion kinase and its potential involvement in tumor invasion and metastasis.Head Neck. 1998 Dec;20(8):745-52. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0347(199812)20:8<745::aid-hed14>3.0.co;2-z. Head Neck. 1998. PMID: 9790298 Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of TRPM7 prevents tumor growth, migration, and invasion through the Src, Akt, and JNK pathway in bladder cancer.BMC Urol. 2020 Sep 9;20(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12894-020-00714-2. BMC Urol. 2020. PMID: 32907556 Free PMC article.
-
A gene signature of cancer-associated fibroblasts predicts prognosis and treatment response in bladder cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Feb;26(2):477-495. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03270-x. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37594617
-
Down-regulation of HOXB5 inhibits TGF-β-induced migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway.RSC Adv. 2018 Dec 11;8(72):41415-41421. doi: 10.1039/c8ra06860g. eCollection 2018 Dec 7. RSC Adv. 2018. Retraction in: RSC Adv. 2022 Sep 30;12(43):27996. doi: 10.1039/d2ra90097a. PMID: 35559288 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
TGF-β and microRNA Interplay in Genitourinary Cancers.Cells. 2019 Dec 12;8(12):1619. doi: 10.3390/cells8121619. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31842336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel immune-related gene pair prognostic signature for predicting overall survival in bladder cancer.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jul 15;21(1):810. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08486-0. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34266411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor A, Jemal A, Bray F. Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: a global overview and recent trends. Eur Urol. 2017;71(1):96–108. - PubMed
-
- Black PC. Fine-tuning risk stratification for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2016;69(1):70–71. - PubMed
-
- Prout GR, Jr, Griffin PP, Shipley WU. Bladder carcinoma as a systemic disease. Cancer. 1979;43(6):2532–2539. - PubMed
-
- Lechertier T, Hodivala-Dilke K. Focal adhesion kinase and tumour angiogenesis. J Pathol. 2012;226(2):404–412. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

