Disialyl GD2 ganglioside suppresses ICAM-1-mediated invasiveness in human breast cancer MDA-MB231 cells
- PMID: 28367091
- PMCID: PMC5370434
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.16903
Disialyl GD2 ganglioside suppresses ICAM-1-mediated invasiveness in human breast cancer MDA-MB231 cells
Abstract
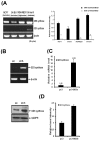
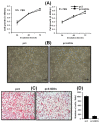
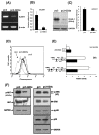
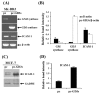
The disialoganglioside GD3 has been considered to be involved in tumor progression or suppression in various tumor cells. However, the significance of the biological functions of GD3 in breast cancer cells is still controversial. This prompted us to study the possible relationship(s) between GD3 expression and the metastatic potential of a breast cancer MDA-MB231 cells as an estrogen receptor negative (ER-) type. The human GD3 synthase cDNA was transfected into MDA-MB231 cells, and G-418 bulk selection was used to select cells stably overexpressing the GD3 synthase. In vitro invasion potentials of the GD3 synthase over-expressing cells (pc3-GD3s) were significantly suppressed when compared with control cells. Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1; CD54) was down-regulated in the pc3-GD3s cells and the decrease in ICAM-I expression is directly related to the decrease in invasiveness of the pc3-GD3s cells. Another type of ER negative SK-BR3 cells exhibited the similar level of ICAM-1 expression as MDA-MB231 cells, while the ER positive MCF-7 cells (ER+) showed the increased expression level of ICAM-1. Then, we investigated signaling pathways known to control ICAM-1 expression. No difference was observed in the phosphorylation of ERK and p38 between the pc3-GD3s and control cells (pc3), but the activation of AKT was inhibited in pc3-GD3s, and not in the control (pc3). In addition, the composition of total gangliosides was changed between control (pc3) and pc3-GD3s cells, as confirmed by HPTLC. The pc3-GD3s cells had an accumulation of the GD2 instead of the GD3. RT-PCR results showed that not only GD3 synthase, but also GM2/GD2 synthase (β4-GalNc T) expression was increased in pc3-GD3s cells. Overexpression of GD3 synthase suppresses the invasive potential of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells through down-regulation of ICAM-1 and the crucial pathway to allow the apoptotic effect has been attributed to accumulation of the GD2 ganglioside. ER has been linked to the ICAM-1 expression with GD3 to GD2 conversion in human breast cancer cells. This is the first finding of the endogenous sialyltransferase functions in tumor cells.
Keywords: Breast cancer; GM2/GD2 synthase (β4-GalNc T); Ganglioside GD3 synthase; Intracellular adhesion molecule-1; Invasion.; MDA-MB231.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction of glycosphingolipids GD3 and GD2 with growth factor receptors maintains breast cancer stem cell phenotype.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 18;8(29):47454-47473. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17665. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28537895 Free PMC article.
-
TNF differentially regulates ganglioside biosynthesis and expression in breast cancer cell lines.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 26;13(4):e0196369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196369. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29698439 Free PMC article.
-
IKK inhibition by BMS-345541 suppresses breast tumorigenesis and metastases by targeting GD2+ cancer stem cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 6;8(23):36936-36949. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16294. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415808 Free PMC article.
-
Ganglioside GD3 synthase (GD3S), a novel cancer drug target.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018 Sep;8(5):713-720. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018. PMID: 30245960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosphingolipids in human embryonic stem cells and breast cancer stem cells, and potential cancer therapy strategies based on their structures and functions.Glycoconj J. 2022 Apr;39(2):177-195. doi: 10.1007/s10719-021-10032-w. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Glycoconj J. 2022. PMID: 35267131 Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of Ganglioside GD2 Synthase (GD2S), as a New Putative Cancer Stem Cell Marker in Breast Carcinomas.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2021 Nov 6;35:148. doi: 10.47176/mjiri.35.148. eCollection 2021. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2021. PMID: 35321364 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-dimensional role of gangliosides in modulating cancer hallmarks and their prospects in targeted cancer therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 27;14:1282572. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1282572. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38089042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does GD2 synthase (GD2S) detect cancer stem cells in blood samples of breast carcinomas?J Appl Biomed. 2021 Dec;19(4):181-189. doi: 10.32725/jab.2021.019. Epub 2021 Sep 16. J Appl Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34907737
-
Emerging role of MAPK signaling in glycosphingolipid-associated tumorigenesis.Glycoconj J. 2024 Oct;41(4-5):343-360. doi: 10.1007/s10719-024-10168-5. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Glycoconj J. 2024. PMID: 39368037 Review.
-
RSRC2 Expression Inhibits Malignant Progression of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Transcriptionally Regulating SCIN Expression.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 19;16(1):15. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010015. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lloyd KO, Furukawa K. Biosynthesis and functions of gangliosides: recent advances. Glycoconj J. 1998;15:627–36. - PubMed
-
- Moon SK, Kim HM, Lee YC, Kim CH. Disialoganglioside (GD3) synthase gene expression suppresses vascular smooth muscle cell responses via the inhibition of ERK1/2 phosphorylation, cell cycle progression, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:33063–70. - PubMed
-
- Ha KT, Lee YC, Kim CH. Overexpression of GD3 synthase induces apoptosis of vascular endothelial ECV304 cells through downregulation of Bcl-2. FEBS Lett. 2004;568:183–7. - PubMed
-
- Moon SK, Kang SK, Kim CH. Reactive oxygen species mediates disialoganglioside GD3-induced inhibition of ERK1/2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. FASEB J. 2006;20:1387–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

