PADI4 Epigenetically Suppresses p21 Transcription and Inhibits Cell Apoptosis in Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- PMID: 28367100
- PMCID: PMC5370443
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.16879
PADI4 Epigenetically Suppresses p21 Transcription and Inhibits Cell Apoptosis in Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Abstract
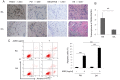
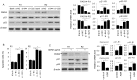
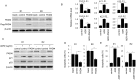
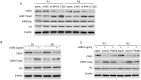
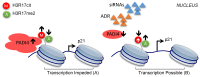
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by synovial lining hyperplasia, which involves abnormal growth of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs). This study aimed to investigate the function and molecular mechanism of peptidylarginine deiminase type 4 (PADI4) in FLSs isolated from RA patients (RA-FLSs). FLSs were isolated from RA patients and transfected with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) or PADI4 overexpression plasmid. FLSs were treated by Adriamycin (ADR) to induce apoptosis, and apoptotic cells were detected by flow cytometry. The expression of PADI4, p53 and p21 was detected by qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis. The recruitment of PADI4 and histone H3 arginine modifications to p21 promoter was measured by chromatin immunoprecipitation. The results showed that knockdown of PADI4 promoted the apoptosis of RA-FLSs and the expression of p53 and p21. Ectopic expression of PADI4 inhibited ADR-induced apoptosis of RA-FLSs, and down-regulated the expression of p53 and p21. In RA-FLSs, global H3 citrullination (CitH3) and H3 arginine 17 methylation levels were dynamically changed by PADI4 and ADR treatment. PADI4 and H3 could bind p21 promoter region to regulate p21 expression. In conclusion, PADI4 contributes to the pathogenesis of RA by protecting FLSs from apoptosis. PADI4 suppresses p21 transcription through altering histone H3 arginine modifications on p21 promoter region. Our study provides new insight into the anti-apoptotic role of PADI4 in RA development.
Keywords: PADI4; cell apoptosis; histone arginine citrullination; p21.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Harris ED Jr. Rheumatoid arthritis, Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1277–89. - PubMed
-
- Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I. et al. Synovial fibroblasts: key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006;45:669–75. - PubMed
-
- Seri Y, Shoda H, Matsumoto I. et al. Peptidylarginine deiminase type4 (PADI4) role in immune system. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2014;37:154–9. - PubMed
-
- Arita K, Hashimoto H, Shimizu T. et al. Structural basis for Ca(2+)-induced activation of human PAD4. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004;11:777–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

